In today’s fast-paced and tightly regulated medical device industry, a Quality Management System (QMS) is far more than a mere compliance exercise, especially for medical device manufacturers. In this article, we will tell you the ins and outs of QMS implementation for medical devices.
It’s truly the backbone of long-term success and innovation. For executives, quality managers, and compliance officers who want to stay ahead of the curve, a well-designed medical device QMS does much more than “check boxes.”
This guide dives deep into what a quality management system for medical devices really entails, why it matters so much, and how to confidently navigate the global regulatory environment.
We’ll explore the core components, best practices for QMS implementation for medical devices, common challenges, as well as the powerful benefits of adopting an electronic QMS (eQMS) over a paper QMS solution to transform your quality processes.
By the end, you’ll see how investing in quality management isn’t just about compliance - it’s about delivering safer, more effective devices and setting your business up for short and long-term success.
What is a medical device QMS, or Quality Management System?
A Quality Management System for medical devices is more than just a regulatory checkbox - it’s the backbone of building safe, effective products that genuinely improve lives.
It ensures that every step of the medical device product development process, from design and development to manufacturing and post-market surveillance is controlled, documented, and continuously improved.
At its core, a medical device quality management system is a structured set of policies, processes, and procedures designed to ensure quality and compliance at every stage of the product lifecycle. But what truly sets it apart is how it’s built to meet the unique demands of the industry and standards like ISO 13485, FDA 21 CFR Part 820, and the EU MDR and IVDR.
Why a QMS matters beyond compliance
However, meeting compliance requirements alone is not enough. A well-implemented medical device quality management system goes beyond satisfying auditors - it becomes a driver of operational excellence, innovation, and trust.
While regulatory bodies require a QMS, the best companies view it as so much more.
Scilife Tip:
When quality is “owned” by everyone, not just a compliance team, your culture shifts toward continuous improvement and accountability.
A strong quality management system for medical devices builds trust among regulators, healthcare providers, and ultimately, patients relying on your devices. It reduces errors and variability, ensures faster problem resolution, and supports ongoing productivity and innovation by providing clear, repeatable processes.
In a competitive market, a mature QMS can accelerate time to market, reduce rework, and demonstrate reliability, becoming a clear differentiator. It's literally the basis of your medical device compliance system.
It also empowers employees at every level by providing clarity about their roles, expectations, and how their work impacts overall quality. In particular, it eases new employee onboarding and transitions of employees from one position to another.

Although getting scolded by your notified body is never fun, the cost of non-compliance is steep and can extend far beyond regulatory citations.
A weak or poorly maintained QMS can lead to delayed approvals, production halts, product recalls, or even market bans. These outcomes damage brand reputation, erode customer confidence and trigger significant financial losses through fines, legal action, and remediation costs.
Moreover, reactive fixes are almost always more expensive than proactive quality management. Investing in a comprehensive medical device quality management system mitigates these risks, protects your bottom line, and lays the groundwork for scalable growth. In the medical device industry, quality is not just a requirement - it’s a strategic asset.
For all our visual learners out there, we have this 5-minute video that explains the basics of a medical device QMS!
Components of a medical device quality management system
A typical QMS consists of a hierarchy of documentation, usually divided into four groups:
- Quality manual: This is your QMS blueprint - a high-level document that defines the scope, structure, quality policy, and objectives of your system.
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): SOPs break down your quality processes into formal, repeatable workflows, covering everything from document control to complaint handling.
- Work instructions: These provide detailed, task-level guidance for employees to perform specific activities consistently and correctly.
- Forms, logs, and records: These serve as proof that processes were followed, decisions were documented, and compliance was maintained.

From paper to digital: QMS implementation for medical devices
Many companies start with a manual or paper-based medical device quality management system. While these can work initially, they often become a headache as companies grow or regulations evolve. Paper gets lost, version control fails, and audits turn into stressful exercises.
An electronic QMS (eQMS) essentially digitizes your quality infrastructure. eQMS platforms centralize documents, automate workflows like CAPA and training, provide real-time visibility into compliance status, and enable faster audit readiness.
The result? Less manual work, fewer errors, more consistent quality, and a system that scales as your business expands.
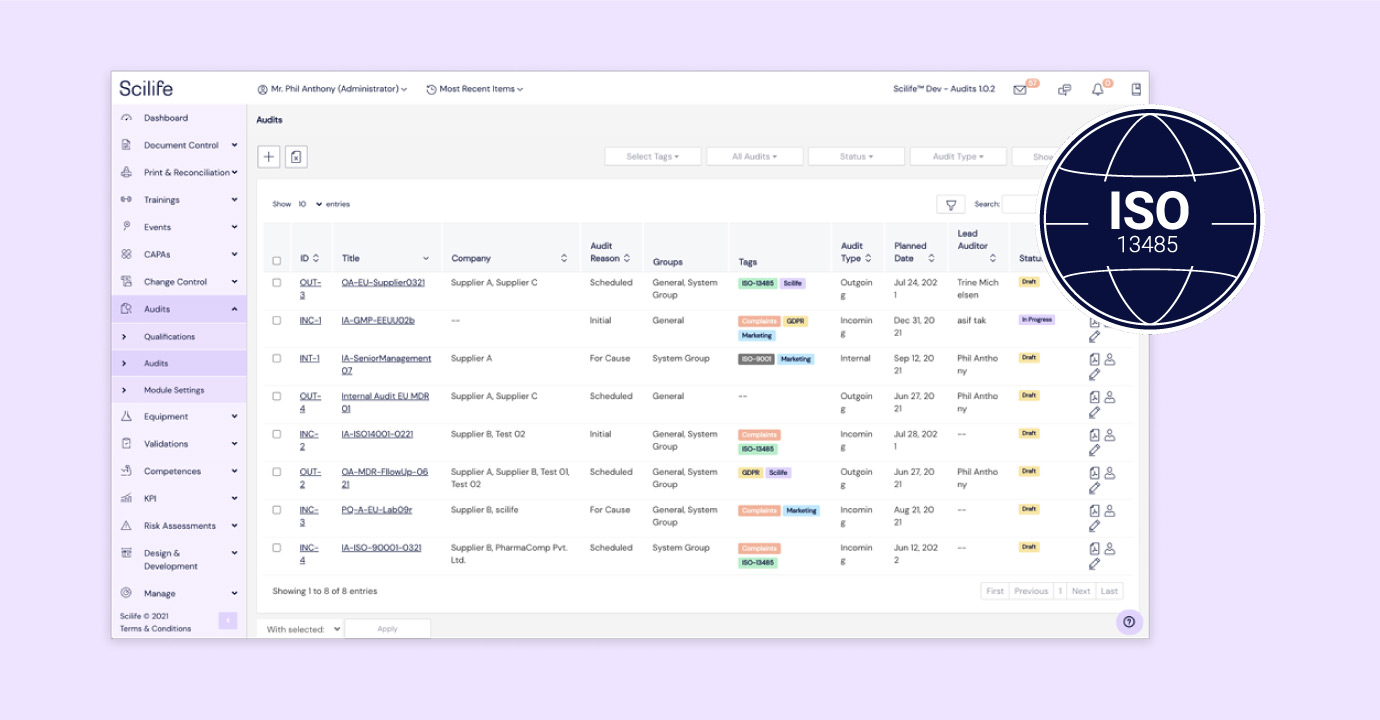
Scilife offers a cloud-based medical device QMS software that helps you manage compliance and ensure product quality throughout the entire device lifecycle — all from one intuitive platform.
Our eQMS is purpose-built for medical device manufacturers, integrating core QMS modules like document control, design & development, CAPA, and supplier management.
Whether you're navigating ISO 13485, EU MDR, or FDA 21 CFR Part 820, we’ve got you covered. Book a personalized demo with our team to see how we can help streamline your quality processes and accelerate time to market.
Medical device QMS as a key part of compliance and product lifecycle management
From concept to commercialization (and long after launch), a strong medical device quality management system ensures that every decision, document, and design element supports safety, quality, and compliance. This is why QMS implementation for medical devices is an important step to a satisfactory product launch and management.
Ensuring product quality and patient safety
At its core, your QMS exists to safeguard patients by making sure your products consistently meet quality standards. It provides the structure and processes needed to design, test, manufacture, and monitor devices, including medical device verification and validation activities, in a way that minimizes risk and promotes continuous improvement.
With tools like design controls, risk management procedures, and change management workflows, a well-implemented medical device quality management system helps you catch issues early before they become costly problems. This type of proactive approach supports better outcomes for patients, clinicians, and your business.
Bringing your device to market faster - and keeping it there
Compliance is non-negotiable in this industry. Regulatory bodies like the FDA, EU regulators, and global notified bodies expect clear documentation, traceability, and evidence that your processes meet stringent quality standards.
A solid medical device compliance system helps you build that foundation and, most importantly, maintain it over time.
Critically, it helps keep your medical device technical file organized, complete, and audit-ready, alongside other critical documents like your audit trails, design history files (DHFs), device master records (DMRs), and device history records (DHRs).
That means faster approvals, smoother inspections, and way less stress when dealing with regulators. It also means you’ll always be able to trace the history of your device and understand why certain decisions were made, even as teams, managers, or production sites change.
If you’d like to learn more about essential medical device documentation — DHF, DMR, and DHR — and how they differ, be sure to read our comparison blog
Supporting the entire medical device product lifecycle
Your medical device quality management system doesn’t stop working or needing maintenance once your product hits the market.
It supports post-market surveillance, complaint handling, CAPA management, and ongoing risk assessment for the entirety of the product lifecycle of your medical device.
These processes not only help you remain compliant, but they also offer valuable insights that feed into product improvements and innovation.
As your business grows or your device evolves, your QMS keeps pace, ensuring that every iteration continues to meet regulatory and quality standards. It’s your long-term partner in building trust with regulators, customers, and patients alike.
In short, your QMS is the thread that ties together quality, compliance, and business success. It’s what helps you not just launch a device, but build a reputation as a strong and reliable company with a medical device compliance system that patients can trust.
Key regulatory requirements governing a medical device quality management system
A strong quality management system for medical devices is a strict regulatory requirement in almost all regulatory markets globally and is championed particularly in the EU and US through ISO 13485 and the FDA 21 CFR Part 820.
No matter where you plan to market your medical device - whether in the U.S., the European Union, or globally - understanding the regulatory landscape is vital, not to mention makes QMS implementation for medical devices simpler.
Although requirements vary across regions, they all share a unified mission: to protect patient health by ensuring that medical devices are safe, effective, and manufactured consistently to the highest standards.
Proactively aligning your QMS with these regulatory frameworks isn’t just about avoiding penalties. It’s a strategic advantage that can streamline product approvals, reduce redundant audits, and open up new markets worldwide. Now let's dive into to all the standards and regulations you must know for your medical device compliance system!

International standards for medical devices: a foundation for global compliance
Here is a brief overview of all the key standards that you should know for your medical device quality management system:
ISO 13485:2016
At the global level, the cornerstone of medical device quality is the ISO 13485:2016 standard. This internationally recognized framework specifies the requirements for a QMS tailored specifically for medical device manufacturers. It emphasizes a process-based approach - planning, monitoring, and continually improving all quality-related activities.
An ISO 13485 quality system system for medical devices covers critical areas like:
- Risk management integration across design and manufacturing
- Supplier controls and qualification
- Control of nonconforming products
- Post-market surveillance and reporting
Considering its importance as a well-known global standard, it’s key to get ISO 13485 right.
Yet many medical companies still fall into common traps that can undermine a medical device compliance system. One of the most overlooked mistakes? Mishandling customer feedback.
To help you steer clear of these pitfalls, we’ve put together an article highlighting the most common ISO 13485 mistakes. Don’t miss it—make sure your processes are aligned and audit-ready.
ISO 14971:2019
But ISO 13485 is just one piece of the puzzle.
Closely linked is ISO 14971:2019, the standard for medical device risk management. It sets out a rigorous process to identify hazards, estimate and evaluate risks, control those risks, and monitor the effectiveness of controls throughout the product lifecycle.
This holistic approach helps manufacturers reduce harm and improve patient safety by systematically managing risk from design through post-market.
Medical Device Single Audit Program (MDSAP)
Another major development improving global efficiency is the Medical Device Single Audit Program (MDSAP). It allows a single audit to satisfy the requirements of multiple regulators, including the FDA (U.S.), Health Canada, Japan’s PMDA, Brazil’s ANVISA, and Australia’s TGA.
By harmonizing audit activities, MDSAP reduces the audit burden on manufacturers and helps get products to market faster and more predictably.
United States: FDA regulations and the evolution to QMSR
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) sets the bar for medical device quality with 21 CFR Part 820, known as the Quality System Regulation (QSR). The QSR mandates that manufacturers establish and maintain comprehensive quality systems, including controls for design, production, process validation, CAPA, and complaint handling.
Recognizing the increasing globalization of medical device markets, the FDA is updating its approach through the forthcoming Quality Management System Regulation (QMSR).
This new framework aims to align U.S. requirements more closely with ISO 13485:2016, simplifying compliance for companies already operating globally. You can read about
The QMSR is expected to:
- Reduce audit duplication and regulatory burden
- Clarify expectations for modern manufacturing and software-driven processes
- Improve consistency between FDA inspections and international audits
For manufacturers, this means proactively reviewing existing QSR compliance, mapping it against ISO 13485 clauses, and training staff on the upcoming changes. Taking these steps early can ease future inspections and support smoother market entry worldwide.
If you’d like to read more about how to prepare for the QMSR and it's harmonization with ISO 13485, don’t miss our article!
European Union: MDR and IVDR - A new era of regulations
Across the Atlantic, the European Union has ushered in a more rigorous regulatory environment with the Medical Device Regulation (MDR 2017/745) and the In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR 2017/746). These medical regulations have replaced previous directives, tightening requirements to better protect patients and improve transparency.
EU MDR
The MDR applies to general medical devices and requires manufacturers to implement robust QMS practices that cover the entire product lifecycle.
Key features of the EU MDR include:
- Strong emphasis on clinical evaluation and evidence collection
- Expanded post-market surveillance and vigilance reporting
- Implementation of unique device identifiers (UDI) for traceability
- Increased oversight by Notified Bodies with greater scrutiny
You can find our guide on the key changes in the EU MDR and important steps to take here.
IVDR
The IVDR focuses on in vitro diagnostic devices and introduces a new risk-based classification system dividing IVDs into four distinct risk classes. It requires extensive clinical performance evaluations and a QMS that supports scientific validity, performance monitoring, and lifecycle management.
Both MDR and IVDR demand agile medical device compliance systems that can quickly adapt to regulatory updates, adverse events, and corrective actions. Many European manufacturers are turning to eQMS platforms to maintain real-time compliance, simplify reporting, and foster collaboration with regulators.
Core processes of a QMS implementation for medical devices
An effective medical device quality management system is built on several tightly integrated core processes. Each plays a crucial role in ensuring your products meet quality and regulatory expectations. These processes don’t exist in silos - they interact continuously to build a cycle of improvement and compliance, which is the key benefit of QMS implementation for medical devices.

1. Document control
At the heart of your QMS is document control. It really is the end-all, be-all part of any quality management system for medical devices. The document control process manages the creation, review, approval, distribution, and archiving of all quality documents, ensuring that everyone has access to the latest, approved versions. Effective document control prevents confusion, reduces errors, and ensures audit readiness by maintaining a clear trail of changes and approvals.
2. Training management
A QMS is only as strong as the people who execute it. Training management tracks employee qualifications and training completion, ensuring that every team member is competent and aware of the latest procedures and regulations. Well-documented training supports audits and helps maintain a culture of quality.
3. Design control
Design control structures your medical device product development process, guiding your team from initial user needs and design inputs to verification and validation. It ensures your devices are safe, effective, and meet customer expectations before manufacturing begins.
4. Risk management
Following ISO 14971, your QMS should include continuous medical device risk management - identifying potential hazards, evaluating their severity and likelihood, implementing controls, and monitoring outcomes. This proactive approach minimizes harm and aligns safety with regulatory demands.
5. Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA)
When things go wrong, and they will (nobody is perfect), CAPA is your tool for investigation and resolution. It involves identifying root causes of nonconformities or complaints, implementing corrective measures, and preventing recurrence. CAPA fosters continuous improvement and builds regulatory confidence.
6. Supplier quality management
Your device quality depends on your suppliers. Supplier quality management evaluates and monitors supplier capabilities, controls incoming materials, and ensures consistency. This reduces risks associated with outsourced components or services.
7. Post-Market Surveillance (PMS)
Even after your device hits the market, quality management continues. Post-market surveillance gathers real-world data on product performance, detects emerging risks, and informs improvements or recalls if necessary. It keeps your QMS responsive and patient-focused.
8. Audit management
Finally, audit management coordinates internal and external audits, tracks findings, and monitors corrective actions. Audits are critical checkpoints that verify your QMS is effective and compliant.
QMS implementation for medical devices: Best practices
Building a medical device quality management system - whether you’re starting fresh or refining what’s already in place - can feel like a big task.
But with a clear step-by-step approach, it becomes much more manageable. The key is to stay focused, bring the right people on board, and remember that quality isn’t just a system - it’s a mindset.
With all of these things in mind, QMS implementation for medical devices doesn't have to feel daunting!

Step 1: Conduct a gap analysis
Begin by taking stock of where you are. What processes are already working well? Where are the gaps compared to regulatory requirements or industry best practices? This initial assessment gives you clarity and helps you prioritize what needs attention without wasting time or effort.
Step 2: Assign ownership and build a team
Quality is a shared responsibility, but having clear leadership is essential. Appoint a QMS champion or create a cross-functional team to guide implementation. Involving people from design, manufacturing, regulatory, and quality ensures well-rounded input and smoother collaboration.
Step 3: Define your quality policy and objectives
Your quality policy should reflect your company’s values and mission - not just tick a compliance box. Set measurable goals that keep everyone aligned and create a strong foundation for continuous improvement.
Step 4: Develop core documentation
This is where your QMS starts to take shape. Create or refine your Quality Manual, SOPs, work instructions, and forms to reflect how your business actually operates. Keep documentation clear, organized, and easy to access - especially during audits or training.
Step 5: Choose the right technology
Manual systems (such as Excel) can work in the early stages, but they often become unwieldy as your company grows. An electronic medical device quality management system (eQMS) can streamline processes, reduce errors, and give you better oversight - all while saving time.
Step 6: Train your team
Your QMS is only as strong as the people using it. Make sure everyone understands their role, the tools they're using, and the "why" behind your quality efforts. Ongoing training helps maintain engagement and keeps your system effective.
Step 7: Validate and test your QMS
Before facing a regulatory audit, do your own internal testing. Conduct internal audits, mock inspections, and validate key processes. This gives you a chance to fix any weak spots and feel confident in your system’s performance.
For additional resources on the best practices and procedures during FDA medical device inspections, read our guide!
Embedding quality into your culture
A successful QMS implementation for medical devices goes beyond checklists and documents - it lives in your company culture. Encourage open communication, make it easy for employees to flag issues or suggest improvements, and recognize wins along the way.
When quality becomes part of how your team thinks and works every day, your medical device quality management system doesn’t just support compliance - it supports long-term success.
Challenges in medical device QMS and how to overcome them
Even the most seasoned medical device professionals know that maintaining a high-performing QMS comes with its fair share of challenges. Regulations evolve, teams grow, resources are cut, and pressure to deliver quickly never seems to ease up. But knowing what to expect from QMS implementation for medical devices- and how to respond - can make all the difference.
Some of the most common challenges of managing a medical device quality management system include:
Keeping up with evolving regulations: new standards, updated guidance documents, and shifting enforcement priorities can feel like moving goalposts. Staying compliant means staying adaptable.
Managing documentation overload: Manual or fragmented systems often result in version control issues, missing records, and a whole lot of time spent chasing paperwork (finding that one document from 8 years ago, when nobody knows the document number or who wrote it, never gets easier).
Engaging employees across departments: Quality isn’t just a “QA thing.” Without buy-in from every team - design, production, marketing, and beyond - your QMS risks becoming siloed and ineffective.
Balancing speed to market with robust quality controls: The pressure to launch quickly can lead to shortcuts or overlooked details, which ultimately cost more time (and money) in the long run.
Supplier quality variability: Even with internal systems in place, your QMS is only as strong as your weakest supplier. Inconsistent materials or processes can ripple through your entire operation.
eQMS: A practical solution that actually works
The good news? These challenges aren’t insurmountable. With the right mindset and tools, your team can tackle them head-on:
- Invest in ongoing training and clear communication: Keep your team informed, involved, and motivated. Training shouldn’t be a one-time event - it’s an ongoing conversation that builds confidence and clarity.
- Adopt an eQMS to streamline and automate: A modern electronic QMS helps reduce manual effort by automating document control, CAPA workflows, audit trails, and training management. It also gives real-time visibility, so you’re never in the dark.
- Foster a culture of accountability and openness: Encourage your team to speak up when something isn’t working. When people feel safe to report issues or suggest improvements, quality becomes everyone’s responsibility - and strength.
- Build risk management into your foundation: Don’t wait for problems to appear. Proactively integrate risk assessment during product design, supplier selection, and every key decision point.
- Use your data as a guide: Your QMS holds valuable insights. Use trend analysis and audit data to uncover patterns, drive improvements, and make informed decisions before small issues grow into big ones.
“I'm a really, really big fan of Scilife’s change requests feature! It really makes changes as an active thing and not just a necessity to be compliant with your QMS. It means we really use it as it is intended by the ISO standard, and not just to be compliant with the ISO standard.”
Ruben Wauthle, co-founder and CEO of Amnovis
While QMS challenges are real, they’re also an opportunity to build smarter, more resilient systems - and teams. With a proactive approach and the right support, quality doesn’t have to feel like a burden. It becomes your competitive edge.
If you’re still on the fence about upgrading to an eQMS (or trying to get your management onboard), check out these Scilife resources to help you make the right decision for your medical device company:
- Top five features of the Scilife eQMS that helps you earn ISO 13485 certification
- 8 reasons why you should turn your paper-based QMS into an eQMS
- Return on investment of having an eQMS
Business benefits of implementing an eQMS like Scilife
Relying on paper-based or disconnected quality systems just doesn’t cut it anymore. More and more companies are making the move to electronic Quality Management Systems (eQMS) to stay competitive, compliant, and efficient.
Scilife’s eQMS is purpose-built for the medical device sector - helping businesses not only meet regulatory demands but thrive within them. It makes QMS implementation for medical devices a walk in the park.
Here’s how an eQMS delivers real value beyond a paper quality management system for medical devices:

Faster certifications and market access: ISO 13485 quality system for medical device
Whether you’re working towards an ISO 13485 quality system for medical devices, FDA approval, or MDR compliance, an eQMS helps speed up the process. By standardizing and automating key workflows, companies can reduce the time and effort needed to demonstrate compliance, bringing medical device products to market faster and with confidence.
Eliminate inefficiencies through automation
Manual processes are not just time-consuming - they’re error-prone. Scilife streamlines document control, audit preparation, CAPA management, and risk assessment, allowing teams to focus less on chasing paperwork and more on strategic tasks that add value.
Reduce regulatory risk
Staying on top of global regulations is a challenge. An eQMS with built-in compliance features helps ensure your processes align with FDA QSR, EU MDR, ISO 13485, and other key standards, reducing the risk of costly delays, non-conformities, or product recalls.
Improve product traceability
From initial design to post-market surveillance, an eQMS offers centralized, real-time access to all quality and compliance records. This complete traceability makes it easy to respond to audits, manage changes, and demonstrate accountability across the product lifecycle.
Scalable for growth
Every company evolves. An eQMS should grow with you - whether you’re a startup preparing for your first certification or an enterprise scaling across markets, flexible solutions adapt to your company’s needs. Choose the tools you need today and expand as your business grows.
“The speed with which we can process documents at SHOEBOX is now almost overwhelming. The actual process of Scilife is lightning fast.”
Sarah Mersereau, Quality and Regulatory Manager at SHOEBOX
The perfect scenario for your quality management system for medical devices
A well-designed medical device quality management system doesn’t just keep you in compliance - it makes your business run smarter. By standardizing processes, automating repetitive tasks, and reducing human error, a QMS frees up time and energy for your team to focus on what really matters: delivering safe, effective medical devices to market - and improving them over time.
With the right QMS in place, every stage of the product lifecycle becomes more efficient.
Design and development are guided by structured documentation and risk controls. Manufacturing benefits from consistent procedures and traceability.
Post-market feedback is captured and looped back into design improvements. That kind of connected thinking accelerates innovation and helps teams make faster, more confident decisions.
An electronic QMS takes this even further, offering real-time access to data, automated workflows, and seamless collaboration across departments.
It’s not just about doing things faster - it’s about doing them better with a robust medical device compliance system.
Win the MedTech race with a QMS that drives growth and compliance
In a complex, rapidly evolving medical device landscape, a well-structured quality management system to manage your medical device compliance system is not just a regulatory requirement - it’s a strategic advantage that drives innovation, safeguards patients, and fuels business growth.
Whether you’re an executive setting the vision, a quality manager designing processes, or a compliance officer navigating regulations, embracing quality management with a modern, scalable approach positions your company for success.
By understanding the core elements of a medical device quality management system, staying ahead of global regulatory expectations, and leveraging digital tools like eQMS, you can build a resilient quality culture that supports continuous improvement and delivers safe, effective devices that truly improve lives.
At Scilife, we partner with medical device companies to simplify quality management and compliance through innovative eQMS solutions. We're here to make your QMS implementation for medical devices simple and stress-free.