Introduction to Audits
An audit is the verification, inspection, or examination of a process, product, or system to guarantee compliance with regulatory or organizational requirements. The scope of an audit can apply to an entire organization or be limited to a specific function, step, or process.
Reasons for Audits
- An internal audit or a first-party audit is performed to measure an organization’s strengths and weaknesses and compare them to internal and/or external standards and procedures. The organization may voluntarily or mandatorily adopt these standards and procedures. These audits are conducted by auditors who are employed by the organization but have no vested interest in the audit findings.
- A vendor audit or second-party audit is performed on a supplier by a customer or contracted company. The goods or services are delivered per an agreed-upon contract. During a second-party audit, customers assess whether the supplier adheres to the standards and procedures that meet customer-defined needs. These audits are more formal than first-party audits because the audit findings could influence the customer's purchasing decisions.
- A regulatory audit or third-party audit is performed by an audit company that is independent of the customer-supplier relationship and free of conflict of interest. In a third-party audit, the auditor is neutral. Organizations use third-party audits to secure certification, registration, recognition, an award, or license approval. However, if non-adherence to the standards and procedures is discovered, the organization may be cited, fined, or penalized.
| First-party Audit | Second-party Audit | Third-party Audit |
| Internal audit | Vendor audit | Regulatory audit |
| Supplier audit | Adherence to a standard audit |
The Importance of Audits
Audits are crucial for all businesses and are especially important for businesses that are in regulated sectors. A financial audit is a minimum requirement for every business, but you may need to prepare for multiple audits. For example, if you are in the life sciences sector, prepare for ISO, US FDA, EMA, MHRA, and other regulatory audits. Additionally, your business may need to schedule internal audits.
Regulated sectors and/or larger markets require more audits. If you are in a regulated sector, such as the life sciences, your success in audits determines your success. If you don't pass the regulatory requirements, you won’t have a product to sell. Audits make or break your business.
Tools for managing supplier audits and corrective action plans
Tools that help manage supplier audits and corrective action plans typically include audit management systems and digital quality management platforms that centralize supplier oversight. These tools support planning and executing supplier audits, documenting findings, and maintaining a clear audit trail across the supplier lifecycle. When issues are identified, they link audit findings directly to corrective and preventive action (CAPA) workflows, enabling root cause analysis, action tracking, and effectiveness checks.
By connecting supplier audits with corrective action management in a single system, organizations can improve audit consistency, ensure accountability, and maintain compliance with regulatory quality requirements. Platforms such as Scilife provide these capabilities by bringing supplier audits, findings, and corrective action plans together within a controlled audit management environment.
What is an Audit Management System?
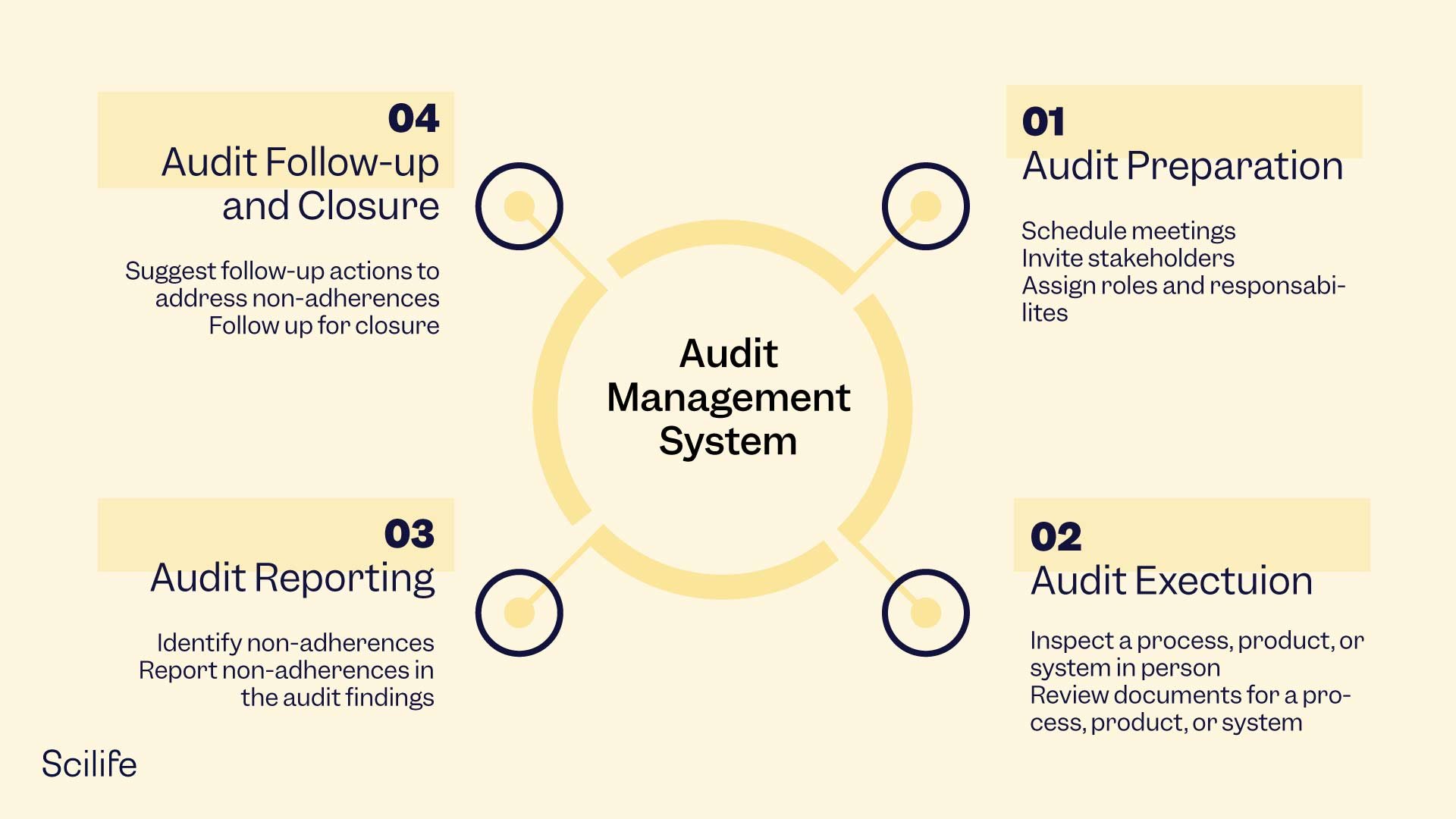
Managing an audit is no ordinary job. The stages are as follows:
- Audit preparation: Planning the date and time for the audit and inviting the lead auditor and auditees.
- Audit execution: Onsite verification of a process, product, or system through physical inspection or document review.
- Audit reporting: Communicating the audit findings in a report and highlighting organizational issues and follow-up actions.
- Audit follow-up and closure: The process ends when no observations are reported by the lead auditor or after follow-up actions are completed.
Successful implementation of these stages requires efficient scheduling, role assignment, document control, and execution. An audit management system (AMS) can help you manage these activities.
The Importance of an Audit Management System
As stated earlier, the success of regulated businesses is determined by the success of audits. Therefore, an AMS is necessary for ensuring that no stone remains unturned. Use an AMS to:
- Schedule your audit within or outside of your e-QMS and send reminder emails.
- Assign roles to your team members.
- Link report components, such as deviations (events) and corrective and preventive actions (CAPAs), to stakeholders and corresponding audits.
- Schedule your next audit.
Advantages of Using an Audit Management System
There are many advantages to using an AMS. Consider the following benefits:
- Save time and resources: An AMS allows you to coordinate teams, organize documents, and schedule meetings without a dedicated human resource.
- Find everything in one place: An AMS reduces the need for other digital tools, such as calendar applications. Everything you need for an audit is included in an AMS.
- Be ready for remote audits: The pandemic increased remote audits, and managing them without an AMS is a Herculean task.
- Receive reminders: Audit findings may require CAPAs. Following up on these actions is stressful because several individuals could be involved. Reminding individuals of pending actions and aligning them on the action plan is an energy-draining process. An AMS sends reminders to individuals and holds them accountable for incomplete actions.
- Foster transparency: Everything is in one place, so data can’t be manipulated. Every document, event, and CAPA has an audit trail that contains information on revisions and includes the names of the creator, editor, and approver. Each change in the document is recorded with time stamps to protect data integrity, which is important for complying with 21 CFR Part 11.
Conclusion
An AMS is the most efficient and convenient tool for preparing for in-person and remote audits. Well-managed audits result in compliant processes, products, or systems, which ensure improved business performance. Better business performance assures customers and secures future prospects for the business. The bottom line: Using an AMS is essential.
In You Can Win, management guru Shivkhera says,
“Winners don't do different things. They do things differently.”
This holds true for managing audits. You don't need a large team to ensure that you are prepared for every audit. You just need one small change, and that change is procuring the right AMS.
Do you know that with Scilife Audit Management Software you can deal with supplier qualifications, supplier audits, internal audits, and incoming audits in just one place?





