Ensuring compliance with 21 CFR Part 11 and EU GMP Annex 11 is crucial for any Life Sciences company using computerized systems in this highly regulated landscape.
Both 21 CFR Part 11 and EU GMP Annex 11 act as safeguards for the Quality, integrity, and safety of products in the Life Sciences. Adhering to these industry standards is not merely a legal obligation – it is a strategic imperative that ensures patient welfare, upholds data accuracy, and fortifies your organization’s reputation and competitiveness
What Is 21 CFR Part 11?
21 CFR Part 11 is a regulation established by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) that governs the use of electronic records and electronic signatures in regulated operations of the Life Sciences. We have put together a detailed overview of 21 CFR Part 11 in this post.
What Is EU GMP Annex 11?
EU GMP Annex 11 is a guidance document that supplements the European Union’s GMP rules and provides guidelines for computerized systems used in GMP-regulated activities in the Life Sciences. It covers various aspects such as electronic forms, documents, signatures, and increased scrutiny of site inspections.
21 CFR Part 11 vs. EU GMP Annex 11
So how do these publications differ? While their names make it easy to mix up the two publications, 21 CFR Part 11 and EU GMP Annex 11 exhibit notable differences in the depth and specificity of their regulatory demands.
Overall, 21 CFR Part 11 stands out for its precise and detailed framework, surpassing the level of general guidance inherent in EU GMP Annex 11. While both standards play pivotal roles in ensuring data integrity and product Quality, 21 CFR Part 11 delves into fine-grained specifics, while Annex 11 offers a panoramic view to steer entities in the right direction.
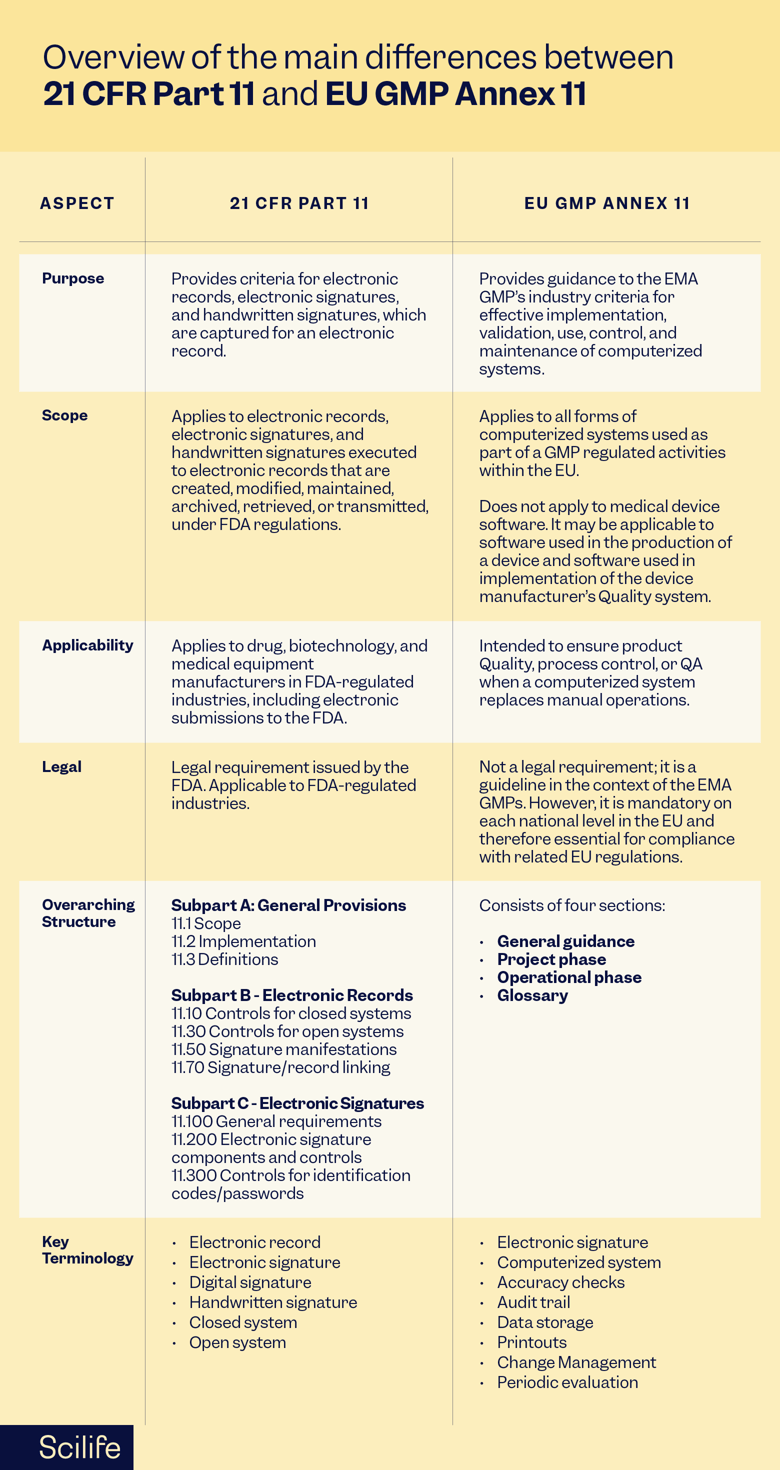
Let’s discuss the most important elements of both frameworks: purpose, scope, applicability, legal, and overarching structure.
Key Aspects of 21 CFR Part 11
Purpose, Scope, and Applicability
21 CFR Part 11 provides criteria for the use of electronic records, electronic signatures, and handwritten signatures, which are captured for an electronic record and are considered “equivalent to paper records and handwritten signatures executed on paper” in FDA-regulated industries.
21 CFR Part 11 applies to electronic records electronic signatures, and handwritten signatures executed to electronic records that are created, modified, maintained, archived, retrieved, or transmitted, under FDA regulations.
The primary reason for 21 CFR Part 11 compliance requirement is promoting the adoption of electronic systems while ensuring security and controlled access, in the distribution, storage, and retrieval of records by drug, biotechnology, and medical devices manufacturers of the digital age in FDA-regulated industries, including electronic submissions to the FDA, but not to paper submissions by electronic methods.
The regulation enhances the overall Quality, transparency, and traceability of electronic documentation.
Legal
21 CFR Part 11 is issued by the FDA and is applicable to FDA-regulated industries, including pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and medical devices.
Overarching Structure
21 CFR Part 11 is divided into three subparts:
- Subpart A – General Provisions discusses the scope of the regulation, the implementation process, and includes definitions of some terms used in the regulation.
- Subpart B – Electronic Records describes the control requirements of users of closed and open systems. It also describes the requirements for signature manifestations and requirements linked to electronic records and signatures.
- Subpart C – Electronic Signatures focuses on general requirements for electronic signatures, electronic signature components and controls, and controls for identification codes/passwords.
Key Aspects of EU GMP Annex 11
Purpose, Scope, and Applicability
EU GMP Annex 11 provides guidance to the EMA GMP industry criteria for effective implementation, validation, use, control, and maintenance of computerized systems.
EU GMP Annex 11 applies to all forms of computerized systems used as part of a GMP-regulated activities. It is not applicable to medical device software. However, it may be applicable for software used in the production of a device and software used in the implementation of the device manufacturer’s Quality system
Annex 11 Is intended to ensure that there is no loss in product Quality, process control, or QA when a computerized system replaces manual operations.
Legal
EU GMP Annex 11 is part of the EU’s GMP guidelines and specifically applies to pharmaceutical manufacturing activities within EU member states and those seeking to export products to the EU market.
Although it is not a legal requirement, it is a guideline related to the EMA GMPs.
Overarching Structure
Annex 11 consists of four sections:
- The first section provides general guidance on topics such as risk management, personnel, suppliers, and service providers.
- The second section provides guidelines for the project phase and operational phase, including best practices for validation.
- The third segment covers best practices for the operational phase and maintenance of computerized systems: accuracy checks, data storage, printouts, audit trails, change and configuration management, periodic evaluation, security, incident management, electronic signature, batch release, business continuity, and archiving.
- The fourth section covers key definitions in the glossary.
How Can You Stay Compliant with 21 CFR Part 11 and EU GMP Annex 11?
Incorporating the principles outlined in 21 CFR Part 11 and EU GMP Annex 11 instills a robust framework for electronic records and signatures management. This framework, meticulously constructed to align with the digital age, bolsters accountability, transparency, and traceability throughout the product lifecycle.
From research and development to manufacturing and distribution, compliance fosters an environment of control and documented evidence, thereby reducing the risk of errors, and non-conformance.
Companies adhering to both frameworks can seamlessly safeguard product Quality through safer electronic data controls and demonstrate a commitment to best practices in computerized systems and data integrity recognized across continents.
Here are some practical tips and indications to help you stay aligned with all requirements with confidence:
Risk Management
Conduct a risk assessment for each computerized system to identify potential vulnerabilities and threats throughout its lifecycle. Develop mitigation strategies and controls to address these risks effectively. Beware to keep risk assessments updated as the system evolves.
Personnel Training and Competency
Provide regular training to personnel who interact with computerized systems. Ensure that these employees understand their roles and responsibilities, especially concerning data integrity, security, and adherence to their duties according to GMP principles.
Supplier Management
Collaborate closely with third-party suppliers and service providers for your computerized systems. Establish clear expectations of the compliance of their products, services, and documentation with Annex 11 and their supplied Quality systems. Conduct audits and assessments of suppliers' Quality systems and validation practices.
Qualification of IT Infrastructure
Perform a rigorous qualification of the IT infrastructure that supports your computerized systems. This involves ensuring that the hardware, software, and network components are appropriately validated to support GMP operations.
Validation Processes
Implement a thorough system validation process for all computerized systems used in GMP-regulated activities. This includes documenting validation plans, user requirement specifications, and validation reports. Engage cross-functional teams (e.g., your IT department, Subject Matter Experts, Process Owners, System Owners, QA) to ensure comprehensive validation, covering aspects like functionality, security, data integrity, and performance.
Data Integrity Assurance
Establish Data Integrity Risk Assessments (DIRA), and establish controls to prevent unauthorized access, alteration, or deletion of critical data. Implement audit trails, electronic signatures, and access controls to maintain the integrity of electronic records.
Procedures and Work Instructions
Develop clear Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) and Work Instructions (WI) for the use of your computerized systems. Ensure that all relevant employees are trained and follow these procedures consistently.
Deviations Management
Establish a process for handling and reporting deviations related to computerized systems promptly. Investigate the root cause of events, implement CAPA actions, and prevent recurrence.
Change Control Procedures
Implement change control procedures to manage any modifications to computerized systems. Changes should be evaluated for their impact on GMP activities, validated if necessary, and documented properly.
Documentation Practices
Maintain complete documentation, including user requirements, design specifications, validation documentation, operational procedures, risk assessments, change controls, deviations, and training. Documentation should be accurate, complete, and readily accessible for inspections and audits.
Backup and Recovery
Develop data backup and recovery procedures to ensure the availability and integrity of electronic records in case of system failures or disasters.
Periodic Review
Conduct periodic reviews of all critical computerized systems to assess their ongoing compliance with Annex 11. Implement a monitoring program to identify and rectify deviations or anomalies promptly.
Audit Trails and Electronic Signatures
Ensure that audit trails are generated for critical activities within computerized systems. Electronic signatures should be implemented where appropriate to ensure accountability and traceability. Evaluate the need and frequency for audit trail review before batch approval.
Internal Audits
Conduct internal audits to computerized systems to identify gaps in compliance with procedures and address them proactively so that you are always ready for inspections.
Key Takeaways
Compliance with 21 CFR Part 11 and EU GMP Annex 11 is vital for preserving product Quality, patient safety, and company reputation.
Specifically, 21 CFR Part 11 governs electronic records and signatures in the FDA-regulated landscape and is more specific, while EU GMP Annex 11 guides computerized systems in the EU's GMP-regulated activities focusing on general guidance, effective implementation, and validation.
And 21 CFR Part 11 is divided into three subparts covering electronic records and signatures; EU GMP Annex 11 is structured into four sections guiding risk management, project and operational phases, and glossary definitions.
To stay aligned with both, we recommend you conduct risk assessments, provide personnel training, manage suppliers, qualify IT infrastructure, implement validation processes, ensure data integrity, follow proper documentation practices, and conduct periodic reviews and audits.
However, interpreting and implementing both frameworks can quickly escalate into a mountain of work that is difficult to overcome. This is why Scilife offers you the required experience and expertise with our Smart QMS. Discover how we can help!