We all know the EU GMP Annex 1 guideline:
Manufacture of Sterile Medicinal Products.
Yet manufacturing is evolving, and new technologies have emerged in recent years. It’s important that companies in the Life Sciences stay on top of these changes.
This brings us to the Annex 1 Revision 2022. The changes therein will take effect on 25 August 2023 (with the exception of section 8.123, which will be enforced starting 25 August 2024).
Continue reading this post for the insight you need to drive Annex 1 2022 compliance within your organization.
Annex 1 Revision 2008: Background
Annex 1 Revision 2008 was completed in December 2007 and went into force in March 2009.
The changes included:
- Alignment with EN ISO 14644-1:1999 (for 5 μm particles)
- A media simulation update
- Bioburden testing adjustments
- Specifications around the capping of vials
Officials have since found that even better regulation is needed—specifically in terms of product shortages, recalls, and GMP non-compliance due to a lack of process understanding.
Annex 1 Revision 2022:
Overview
A reminder that the Annex 1 Revision 2022 will take effect on 25 August 2023, with section 8.123 being postponed to 25 August 2024.
The reasons for the changes in the Annex 1 Revision 2022 are twofold:
- Manufacturing technologies and GMP have both advanced considerably since 2008—including ISO 14644, ICH Q9, and ICH Q10.
- The EMA, PIC/S, and WHO sought a complete rewrite with significant business input.
Now let’s go over the actual changes in the Annex 1 Revision 2022:
- Expansion from 16 to 51 pages (not including the glossary)
- Multiple new and extended topics
- Focus on contamination risk management
You’ll find an emphasis on Quality Risk Management (QRM) throughout the entire document. The main purpose is to set standards for sterile products and the added applicability to non-sterile products.
What Does the Annex 1 2022 Revision Include?
The goal of the revision was to eliminate inconsistency and acknowledge technological advancements.
Now let’s discuss the key sections involved:
Principles
This section represents the ideology behind the new Annex 1. Essentially, it states that sterile products should be produced in a qualified environment by trained personnel using conscious, traceable processes and adequate control of materials.
Please note that Annex 1 applies to the entire supply chain—from manufacturing to packaging and logistics. This means there must be a focus on the contamination control strategy.
The revision also states that validation and qualification are no longer one-off events and that personnel must be well-trained. In addition, QRM must be incorporated into the Quality Management System (QMS) throughout the entire document.
Pharmaceutical Quality System
This section should be read in conjunction with GMP Chapter 1. It states that the QRM process should assess the facility, personnel, processes, and monitoring to identify and control risks.
Quality Assurance (QA) oversight may be somewhat murky here—but as the final client, you are responsible for addressing it explicitly.
In turn, the Contamination Control Strategy (CCS) must be part of the overall management review.
Premises
This section recommends the use of new technologies to prevent contamination in Grade A areas.
- Grade A
Classification areas represent a “critical zone” for high-risk operations. They also feature unidirectional airflow. - Grade B, C, and D
Classification areas, meanwhile, are “cleanrooms” that feature the unidirectional transfer of materials and personnel into designated areas via airlocks.
Speaking of premises, new technologies like isolators and RABS (Restricted Access Barrier Systems) play an integral role in the Annex 1 Revision 2022. There is a significant expansion of the section describing isolators and RABS, plus some background on the difference between the two technologies.
Please understand that there are some changes in the classification requirements too. The 5 μm particle no longer has specified limits for grades A/B at rest, for example. The table below reflects other minor changes.
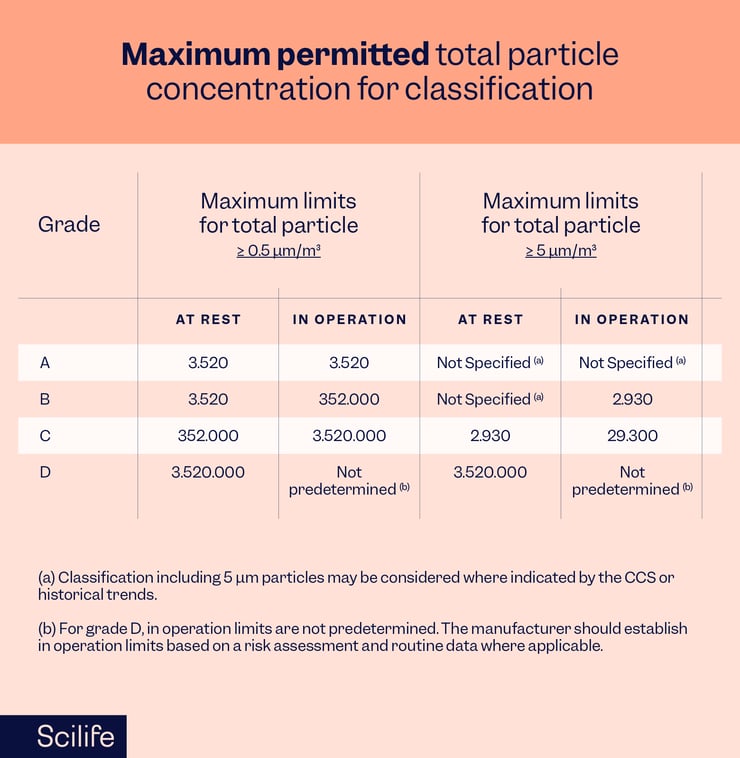
Microbial concentration levels must also be determined during qualification.
Equipment
This section states that direct and indirect product contact parts should be sterilized after reassembly when possible.
The default regulatory exception is sterilization, which may require extensive process changes.
As directed, plan to rely on QRM strategies. When in doubt, you may contact your local regulatory agent and ask for help.
Utilities
This update is a big one. The new Annex 1 has a new chapter on “Utilities,” or the required equipment and materials that may come into contact with a product.
Water systems, steam, compressed gas, and vacuum and cooling systems are essential considerations here.
Personnel
The Annex 1 Revision 2022 places significant emphasis on people—complete with a new focus on training and gowning. Keep in mind that there must be trained and experienced people working in every aspect of your production.
In addition, new gowning requirements include:
-
- Facility socks for entry into Grade C areas or higher
- Sterile goggles in Grade B areas
- Glove disinfection
Your organization must also define the maximum time cleanroom garments can be worn in Grade A and B areas.
Production & Specific Technologies
The former Annex 1 indicated that operations performed in Grade A areas were minimal.
The list of required operations has been extended in Annex 1 Revision 2022—and Grade B requirements were added too.
New operational requirements include:
-
- Aseptic preparation
- The design process (using technical solutions like robotics)
- Sterilization techniques
- PUPSIT (Pre-Use Post-Sterilization Integrity Testing)
PUPSIT and 100% integrity testing are crucial to Annex 1 Revision 2022. While PUPSIT features certain risks, the benefits are extensive. This is because the current controls during filter manufacturing, transport, and installation are not sufficient to protect against minor flaws.
An unbiased risk assessment can take place if PUPSIT testing is not possible (for example, if PUPSIT testing would result in the dilution of your product).
With this in mind, an Annex 1 Revision 2022 subsection was added on single-use systems (which are usually outsourced).
Officials added another subsection on closed systems—reducing the need for aseptic connections. These systems are prepared in-house and sterilized after assembly.
Viable and Nonviable Environment & Process Monitoring
The Annex 1 Revision 2022 states that your organization’s Contamination Control Strategy (CCS) should include an explicit description of your organization’s monitoring program.
This must include factors such as:
-
- Environmental monitoring (total particle)
- Environmental and personnel monitoring (viable particle)
- Temperature, relative humidity, and other characteristics
- Aseptic Process Simulation (APS) (only for aseptically-manufactured products)
APS should be repeated twice per year for every aseptic process, filling line, and shift. Moreover, each operator should participate in at least one successful APS on an annual basis.
Quality Control
This section is the Quality Control (QC) part of the new Annex 1.
It includes requirements on:
-
- QC/QA personnel training and experience
- Specifications
- Types of microbiological tests
- Sampling
- Method verification and validation
- Parametric release
- Data review
Conclusion
In conclusion, these are the key factors to consider when driving Annex 1 Revision 2022 compliance. It is important, however, to remember that the new Annex only lays out the minimum manufacturing requirements for sterile medicinal products. The truth is that manufacturing these products is about so much more than continuous improvement. To this end, organizations should continue to focus on preventative strategies, including risk assessments, corrective and preventive actions (CAPAs), and more.
Find out how Scilife Smart QMS can help you comply with Annex 1!