What is Pharma 4.0?
Pharma 4.0 is the trademark of an initiative from the International Society for Pharmaceutical engineering (ISPE). Pharma 4.0 refers to the use of Industry 4.0, also called Smart Factory technologies, to improve quality and efficiency in the pharmaceutical industry.
Many organizations are embarking on a digital transformation journey towards a Pharma 4.0 strategy. What is its origin?
The strategy originally comes from the term Industry 4.0, also known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution. Industry 4.0 represents a shift towards a more interconnected and digitized industrial landscape, where smart factories and advanced manufacturing techniques are able to optimize production and improve efficiency through the use of data analytics and machine learning.
This Fourth Industrial Revolution brings significant changes in the way businesses operate and how products are designed, manufactured, and delivered to customers.
In Pharma, it represents a new era of human advancement, where automation and data exchange are applied as enablers in manufacturing technologies, including developments in artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and cybersecurity to improve the current Pharmaceutical Quality System (ICH Q10).
These novel technologies can be leveraged to control pharmaceutical operations free of any human intervention, with an improvement in the efficiency, safety, and effectiveness of drug development and manufacturing, as well as to enhance the overall patient experience.
The advantages of following the Pharma 4.0 roadmap help organizations to take data-driven decisions, based on real-time data, across the product life cycle and focus on holistic oversight of product quality and performance. The goal is to create a patient-centered pharmaceutical industry through the use of advanced technologies.
Pharma 4.0 technologies are being used for predictive analytics, smart manufacturing, virtual reality, simulation, and patient engagement.
For example:
Predictive analytics: Machine learning algorithms analyze large amounts of data from various sources (e.g. clinical trials, electronic health records) to identify patterns and trends that can inform drug development and patient care.
Smart manufacturing: IoT technologies monitor and optimize the drug manufacturing process. Sensors are used to track temperature, humidity, pH, and other environmental conditions that can affect the quality of the final product.
Virtual reality and simulation: these novel technologies can be used to train Life Sciences employees, design and test manufacturing processes, and simulate patient experiences.
Patient engagement: digital platforms, mobile apps, telemedicine, and other new technologies enhance patient engagement.
Why is Data Integrity important to Pharma 4.0?
Data integrity is a critical aspect in current life sciences and also in the transition to Pharma 4.0. It helps to ensure that data that is generated and used to drive the advanced manufacturing processes and decision-making systems, is trustworthy and complies with ALCOA principles (attributable, legible, contemporaneous, original, and accurate). If you're eager to dive into the key elements of a pharmaceutical QMS, dive straight into our QMS in pharma guide.
In the pharmaceutical industry, data integrity is crucial for ensuring the quality, safety, and efficacy of medicinal products. Compliance with data integrity regulations, such as 21 CFR Part 11 and EU GMP Annex 11, helps mitigate risks associated with data manipulation, errors, and breaches. Adhering to these standards also reduces the likelihood of costly regulatory actions, such as product recalls, warning letters, or rejected approvals.
If data integrity is compromised, it could lead to incorrect decisions being made, which could have serious consequences for both the manufacturer and the end patient.
Some of the benefits of maintaining data integrity in the transition to Pharma 4.0 include:
Quality: Maintaining data integrity helps ensure that the products being produced meet the required standards for quality and safety.
Efficiency: Reliable data enables advanced manufacturing systems to operate more efficiently, reducing waste and increasing productivity.
Compliance: Maintaining data integrity helps ensure that manufacturers are in compliance with regulatory requirements.
Trust: Data integrity helps build trust with customers, partners, regulators, and patients, which is essential for maintaining a good reputation and long-term success.
What are the challenges of applying Data Integrity in Pharma 4.0?
There are several challenges that organizations may face when applying Data Integrity principles in the context of the transition to Pharma 4.0. Some of these challenges include:
Compliance with regulations: Ensuring data integrity is essential for regulatory compliance. Companies must be able to continuously demonstrate to regulatory agencies that they have robust data integrity systems in place.
Managing large volumes of data: Pharma 4.0 involves the collection, review, and analysis of large volumes of data from various sources, including sensors, connected devices, platforms, and machine learning algorithms. Managing this data is a challenge, especially in terms of ensuring its accuracy and reliability.
Ensuring the quality of data: Ensuring the quality of data can be a challenge when multiple sources of data need to be integrated and analyzed.
Ensuring data security: It becomes increasingly important to ensure the data generated and analyzed is safe. This includes protecting it from cyber threats, as well as ensuring that it is only accessed by authorized personnel.
Managing the integration of new technologies: The transition to Pharma 4.0 involves the integration of novel technologies, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the Internet of Things, into the quality and manufacturing process. Managing the integration and validation of these technologies and ensuring that they are used effectively can be a challenge. The use of real-time monitoring, using connected systems must enable an agile continuous manufacturing system.
Overall, applying data integrity principles in the context of Pharma 4.0 requires a comprehensive approach that takes into account the efforts of transformational teams. Companies must be prepared to invest in the new systems and processes, with a focus on validation requirements that provide evidence of the who, what, where and when of each action.
What is the digital maturity level of organizations?
According to ISPE, digitalization in the Pharma industry is quite immature. The pharmaceutical sector is still very conservative. Innovation has not been adopted as quickly as in other sectors mainly due to compliance oversight: GxP regulations, validation processes, and patient safety have played a role in delaying exploring and implementing Pharma 4.0 initiatives.
For example: there are still some companies that have a limited or poor communication system among their different functions, no training for risk management, no risk governance for data management, or no information security measures against cyberattacks. Regarding quality culture, their culture of an “open” and “collaborative” mode of work is still fragile.
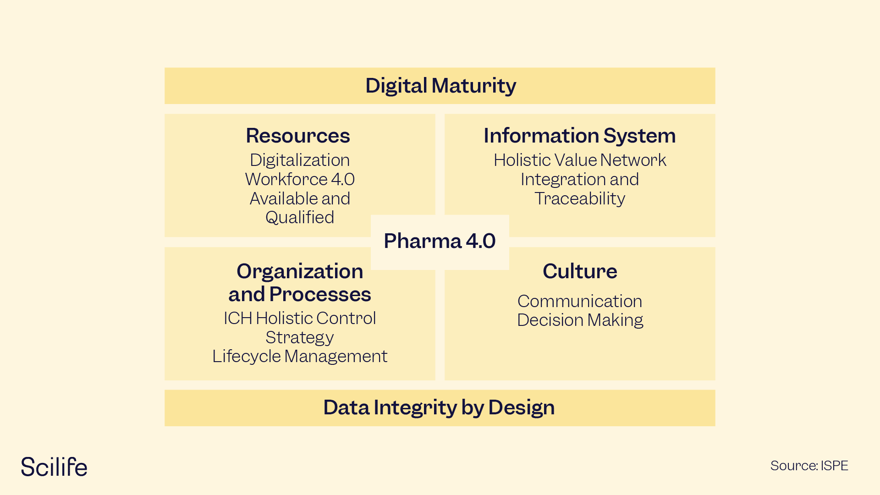
This is why ISPE’s Pharma 4.0 initiative has designed a Pharma 4.0 Operating Model that describes some key enablers to improve Pharma processes and culture.
Pharma 4.0 takes a holistic approach to the implementation of digital technologies and a digital mindset within Pharma.
The framework is based on the four elements of the ISPE Pharma 4.0 Operating Model and two enablers:
1.- Resource
2.- Information Systems
3.- Organization and Processes
4.- Culture
The enablers are Digital Maturity and Data Integrity by Design (see Figure 1).
This leads to the concept of Digital Maturity, which refers to an organization's level of progress in adopting and integrating digital technologies and practices into its operations.
It ranges from minimal use of computers and automation to a completely digital autonomous Pharma plant that adapts on its own to changing manufacturing conditions.
The model is based on questionnaires with closed or open answers. The assessment provides a final digital maturity index that can be used for benchmarking studies.
Figure 1. The Pharma 4.0 Operating Model.
How do you measure the digital maturity level of organizations?
There are many ways to measure digital maturity, but ISPE started using the Industry 4.0 Maturity Index created by ACATECH.
ACATECH’s Maturity Index is made up of a set of criteria that are used to evaluate a company's progress in adopting Industry 4.0 technologies and practices. These criteria include things like the extent of automation and digitalization in the company's processes, the use of data analytics and AI, and the level of connectivity and interoperability within the company's systems.
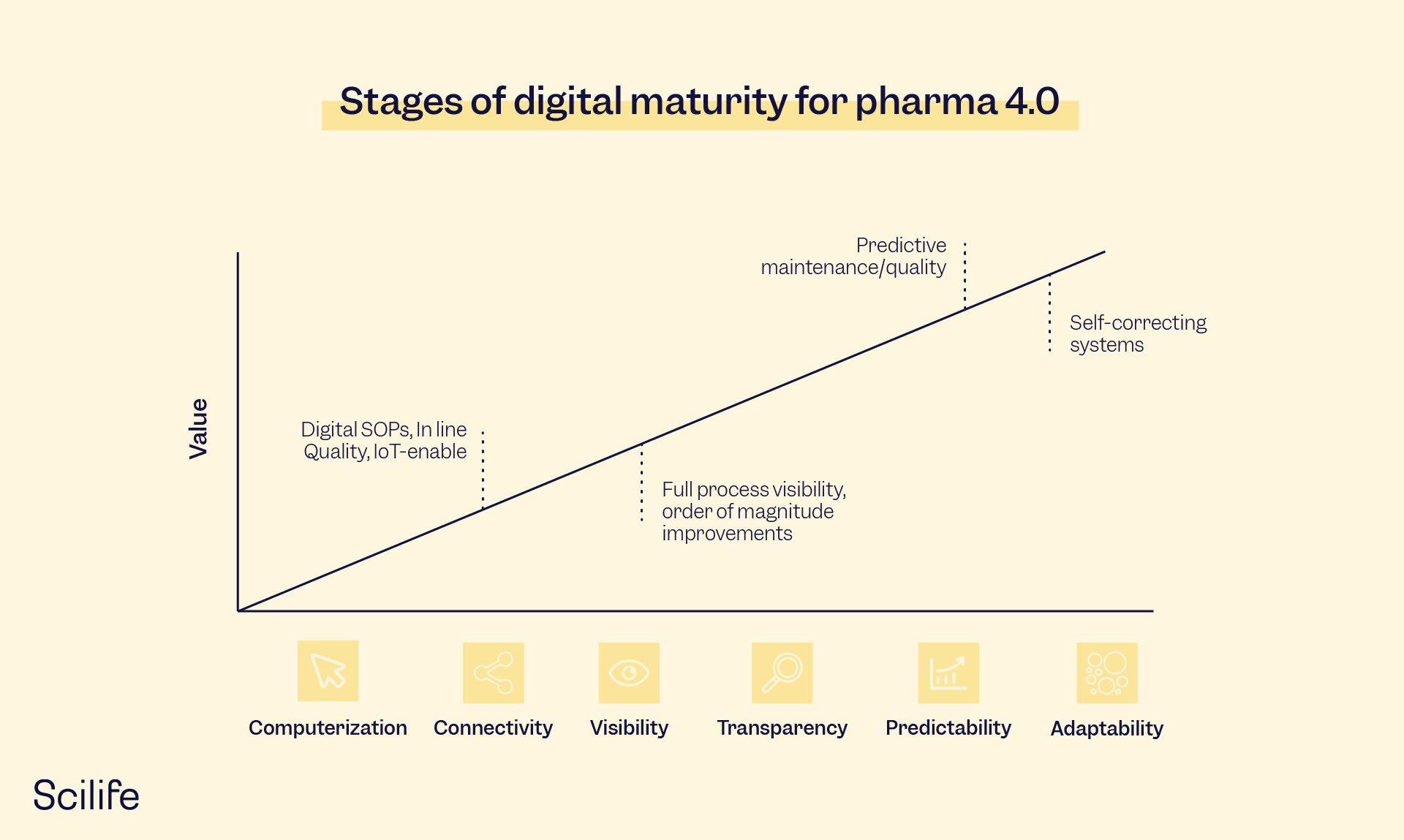
Figure 2. Stages of Digital Maturity
The Index is based on a six-stage maturity model. It analyzes the capabilities in the structural areas of resources, information systems, culture, and organizational structure that are required by organizations operating in a digitalized industrial environment:
Level 1: Computerization
Level 2: Connectivity
Level 3: Visibility
Level 4: Transparency
Level 5: Predictability
Level 6: Adaptability
The ISPE Pharma 4.0 Maturity Index Working Group is still working to create a Maturity Index that can level the degree of digitization of pharmaceutical organizations and identify improvement areas to fully transform them into a digitalized and paperless organization.