In the fast-paced and highly regulated world of pharmaceuticals, ensuring the highest standards of quality is paramount. Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance (QA) leaders face a myriad of challenges in maintaining compliance, minimizing risks, and delivering safe and effective products to patients. Why is managing Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance so difficult?
One of the reasons could be that some Pharmaceutical companies rely on manual and paper-based systems that can’t keep up with the pace of change. This results in compliance gaps, quality issues, and costly mistakes. Document management is tedious and error-prone. Training, change control, and risk management lack connectivity and visibility. As the antiquated quality systems are unable to manage electronic records 21 CFR Part 211 or seamlessly connect data for more efficient decision-making. A smarter solution is urgently needed.
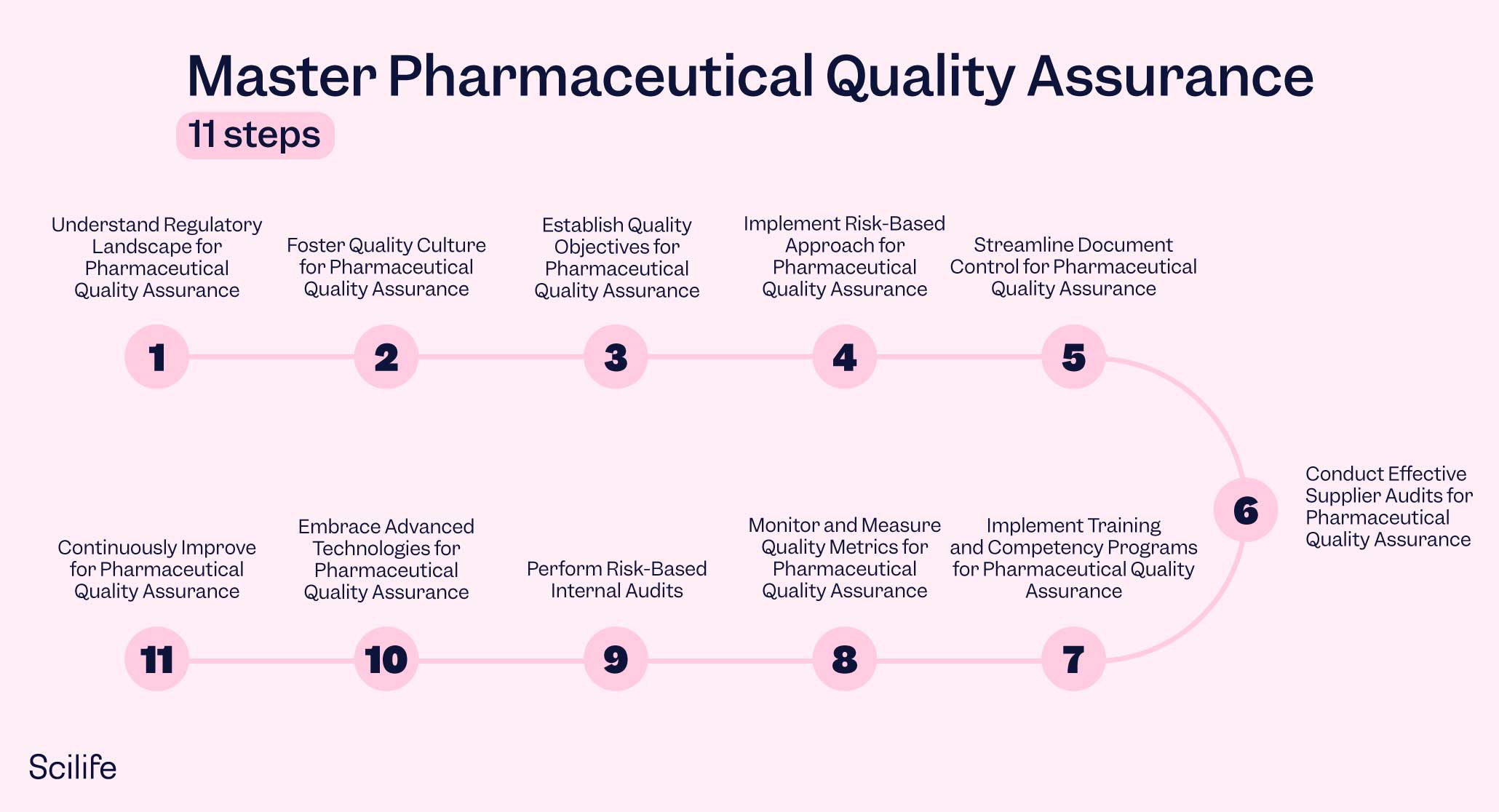
In this blog post, we will delve into the common problems faced by Pharmaceutical QA leaders and suggest 11 easy steps to implement smart Quality Management software as a compelling solution to overcome these challenges. By following these 11 steps, you can master Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance and drive excellence in your organization.
And if you want to dive even further into building and maintaining a QMS in pharma, check out our full guide!
Step 1
Understand Regulatory Landscape for Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance
The pharmaceutical industry operates within a complex regulatory landscape. Stay informed about current regulations, guidelines, and standards from regulatory bodies such as the FDA, EMA, and other relevant authorities. This understanding will form the foundation of an effective Quality Assurance strategy. Our guide to QMS in pharma breaks down all the regulations, standards and guidelines that you need to know.
Knowing the regulatory landscape is immensely advantageous for a Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance. Firstly, it ensures compliance with the complex and ever-evolving regulations, guidelines, and standards set by regulatory bodies. By staying updated on regulatory requirements, the QA leader can develop and implement robust quality systems that meet the necessary standards, minimizing the risk of non-compliance and potential penalties. Additionally, understanding the regulatory landscape enables the QA leader to proactively identify and address any gaps in their organization's quality processes, ensuring the safety, efficacy, and integrity of pharmaceutical products. It also facilitates smooth and efficient interactions with regulatory agencies, as the QA leader can navigate the regulatory landscape with confidence, engage in meaningful dialogue, and effectively communicate the organization's commitment to quality. Ultimately, knowledge of the regulatory landscape empowers the QA leader to foster a culture of compliance, maintain the reputation of the organization, and safeguard the well-being of patients.
Step 2
Foster Quality Culture for Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance
Quality must be ingrained in the organization's culture. When quality is ingrained in your organizational culture, employees see it as a moral responsibility and not only as a mandatory compliance requirement. Therefore, promote a quality mindset at all levels, encourage employees to take ownership of quality and champion continuous improvement initiatives. Foster a culture that prioritizes patient safety and product quality above everything else. When everyone starts doing the right thing first, then you will see employees working with increased vigilance and attention to detail, as a result you will see a reduced number of errors, defects, and deviations in the production and testing processes. Moreover, a quality mindset encourages proactive problem-solving and the identification of opportunities for process optimization, ultimately driving operational efficiency.
Step 3
Establish Quality Objectives for Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance
Define clear quality objectives aligned with the organization's mission and strategic goals. These objectives should be specific, measurable, actionable, and time-bound, providing a roadmap for the entire Quality Assurance function. Ensure to state your Quality Objectives in a clear and concise manner in your organization’s Quality Policy. Here is an informative blog post on how you can establish SMART Quality goals or objectives for your organization.
Step 4
Implement Risk-Based Approach for Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance
Adopt a risk-based approach to quality management. Identify and assess risks throughout the product lifecycle, including formulation, manufacturing, packaging, and distribution. Develop corresponding risk mitigation strategies and allocate resources accordingly.
Read this article to understand how you can implement a risk-based thinking approach for Quality Management in your organization. You may also want to take a glance at the most frequently used risk management tools in the life science industry.
Step 5
Streamline Document Control for Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance
Documents are an important resource for almost every task we do in our workplace. One of the key principles of having a robust Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance Process is to do what the documents say. Any gaps between written procedures and actual execution may be good enough for raising suspicion during audits and inspections. Since, we refer to several Standard Operating Procedures, Work Instructions, Reports, etc., to leverage necessary information for executing our tasks, it is absolutely imperative to implement an e-QMS or smart Quality Management software to streamline document control processes. It helps to centralize document management, version control, and approvals while ensuring that only the most up-to-date and approved documents are accessible to relevant stakeholders. In addition, it also provides a high level of transparency, traceability, and clarity for performing everyday tasks in the workplace.
Step 6
Conduct Effective Supplier Audits for Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance
Develop a robust supplier management program. Perform thorough supplier audits to assess their quality systems, capabilities, and adherence to regulatory requirements. Establish clear criteria for supplier selection and ongoing evaluation. It will go a long way to monitor and maintain the quality of critical input materials that have an impact on your finished product quality.
Step 7
Implement Training and Competency Programs for Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance
You might have heard the famous quote by Abraham Lincoln: “Give me six hours to chop down a tree and I will spend the first four sharpening the axe.” Providing employee training for Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance is also equivalent to ‘Sharpening the Axe’ that Lincoln mentioned.
Therefore, invest in training and competency programs to ensure employees possess the necessary skills and knowledge to perform their roles effectively. Provide ongoing training on quality systems, regulations, and best practices.
Step 8
Monitor and Measure Quality Metrics for Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance
Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) and quality metrics to monitor and measure quality performance. Regularly review and analyze these metrics to identify trends, areas for improvement, and to drive data-driven decision-making.
Step 9
Perform Risk-Based Internal Audits
Conduct regular internal audits using a risk-based approach. Identify gaps in compliance, evaluate the effectiveness of quality systems, and drive continuous improvement. Develop robust corrective and preventive action plans based on audit findings.
Step 10
Embrace Advanced Technologies for Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance
Leverage innovative technologies to enhance Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance processes. Explore the possibilities of automation, artificial intelligence, and machine learning to improve efficiency, accuracy, and compliance.
Step 11
Continuously Improve for Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance
Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance is a journey of continuous improvement. Foster a culture of learning, encourage feedback, and actively seek opportunities for optimization. Regularly review and update quality processes and systems to stay ahead of evolving regulatory requirements and industry best practices.
Conclusion
Mastering Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance requires a strategic and systematic approach. By following these 11 steps, you can navigate the complexities of the industry, achieve compliance, and deliver safe and effective pharmaceutical products. Our smart Quality Management software is designed to empower Pharmaceutical QA leaders on this journey. Take action today, embrace our solution, and unlock unparalleled efficiency, compliance, and quality performance as one of the best quality management software on the market for pharma.
Remember, excellence in Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance is not a destination but a continuous pursuit. Stay informed, adapt to emerging trends, and embrace innovative technologies to stay ahead in an ever-evolving industry. Together, let's ensure patient safety and drive the highest standards of quality in pharmaceuticals.