International Council for Harmonization (ICH)
The International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) is a global organization that integrates all regulatory agencies and the pharmaceutical sector to provide standards and guidelines for the creation, registration, and post-approval of pharmaceutical products.
History
The ICH was established in 1990 as a collaboration between regulatory authorities and the research-based pharmaceutical industry, with the goal of achieving greater harmonization of requirements and guidelines across different regions and countries.
ICH has consistently changed to adapt to more widespread innovations in the pharmaceutical industry, and an increasing number of regulatory authorities are using these ICH principles.
Mision
The goal of ICH is to promote global harmonization in order to ensure that high-quality, safe, and effective pharmaceuticals are created, registered, and maintained in the most resource-effective way possible while upholding strict criteria. The ICH has expanded as an organization after announcing organizational reforms in October 2015. There are now 20 Members and 36 Observers.
Funding
The ICH Assembly is in charge of approving the ICH Association's yearly budget, the amount of the membership dues, and other funds to be raised for the upcoming fiscal year. The ICH Association is supported by annual membership fees. Based on drafts created by the ICH Management Committee, the annual budget is approved by the ICH Assembly.
The four categories listed below are used to categorize the ICH topics and assign ICH topic codes to each of them:
Quality Guidelines
The performance of stability studies, the establishment of necessary impurity testing thresholds, and a more flexible approach to pharmaceutical quality based on Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) risk management are all significant milestones in the harmonization of the Quality domain.
Safety Guidelines
In order to identify potential dangers including carcinogenicity, genotoxicity, and reprotoxicity, ICH has created a thorough set of safety guidelines. A non-clinical testing approach for determining the QT interval prolongation liability - the leading factor in drug withdrawals in recent years -has made significant strides recently.
Efficacy Guidelines
The design, conduct, safety, and reporting of clinical trials are all topics covered by the work done by ICH under the Efficacy umbrella. Additionally covered are novel drug classes produced by biotechnological methods and the application of pharmacogenetics and genomics to the development of more precise drug formulations.
Multidisciplinary Guidelines
Those are the topics that cut across all three of the other categories - Quality, Safety, and Efficacy - and are therefore considered to be cross-cutting. The creation of Electronic Standards for the Transfer of Regulatory Information (ESTRI), the Common Technical Document (CTD), and the ICH medical terminology (MedDRA) are all included in this.
ICH Guideline Implementation
ICH Regulatory Members and Observers execute ICH Guidelines in their specific nation or region. This is in keeping with the purpose and goal stated in the ICH Articles of Association, which calls for all ICH Regulatory Members to apply all the ICH Guidelines. Implementing (certain) ICH Guidelines is a requirement for ICH Regulatory Observers before they may join the organization as a regulatory member.
The stage of implementation of each ICH Guideline also depends on when a Member or Observer joined ICH. ICH Guidelines are implemented in accordance with the applicable national, local, and regional laws.
ICH Standards
MedDRA (Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities)
In order to improve the international exchange of regulatory information for medical products used by humans, ICH created MedDRA, a comprehensive and highly detailed standardized medical terminology. It is utilized both before and after a product has been given the go-ahead for sale for the registration, documentation, and safety monitoring of medical items. Pharmaceuticals, vaccines, and drug-device combination items are all included in the scope of the MedDRA.
To maintain, create, and disseminate MedDRA, the ICH formed the MSSO (Maintenance and Support Services Organisation), which was given technical and financial oversight by the MedDRA Management Committee. MedDRA is regularly improved to meet the changing demands of regulators and industry around the world under the direction of the MedDRA Management Committee. Free training is provided, and MedDRA is currently offered in many languages other than its original English translation, including Chinese, Czech, Dutch, French, German, Hungarian, Italian, Japanese, Korean, Portuguese, Brazilian Portuguese, Russian, and Spanish. This helps to further facilitate its implementation and proper use. Should the MedDRA Management Committee receive interest, additional translations will be taken into account.
Collaboration of ICH and WHO
The WHO worldwide safety database completely integrates MedDRA, enabling data entry and retrieval in either MedDRA or WHO-ART. Users can easily convert their data and use MedDRA since WHO and ICH maintain an updated mapping bridge that enables conversion of WHO-ART coded data.
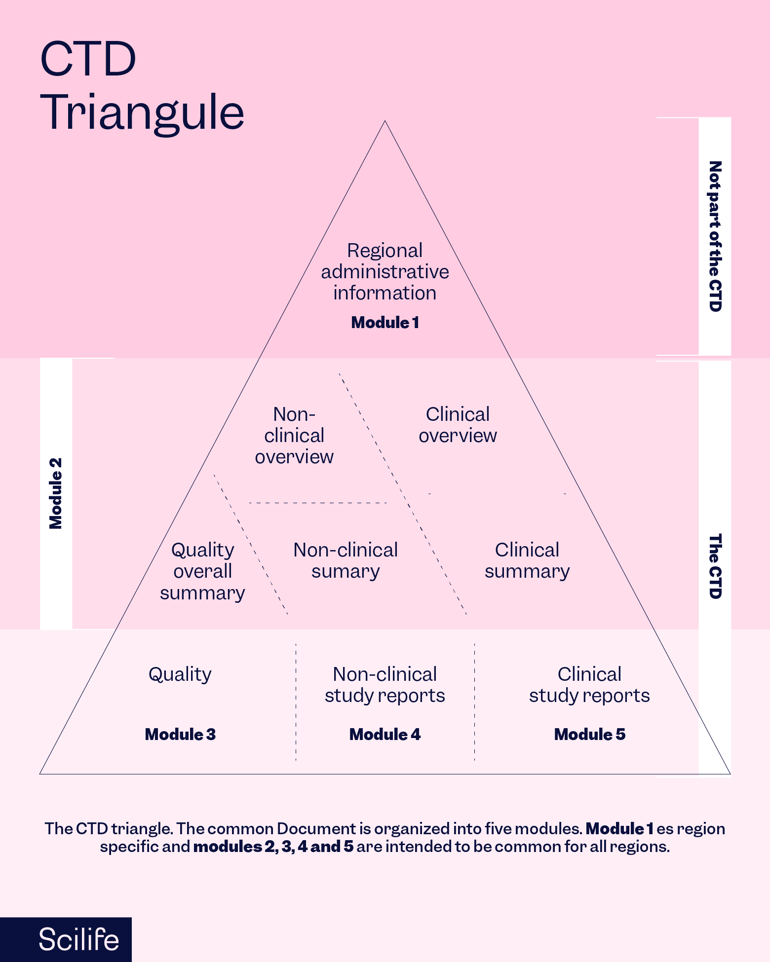
The Common Technical Document
The decision to compile all Quality, Safety, and Efficacy data into a single document, known as the CTD (Common Technical Document), transformed the regulatory review procedures and allowed for the adoption of best review practices through standardized electronic submission. For businesses, it has removed the requirement to alter the data before submitting it to the various ICH regulatory bodies.
There are five modules in the CTD. Modules 2, 3, and 4 are meant to be universal for all regions, but Module 1 is region-specific. The CTD became the preferred format for NDAs submitted to the FDA in the United States and the EU in July 2003, and it is now required for new drug applications in Japan and the EU.
Electronic Standards (ESTRI)
The harmonization of Electronic Standards is the focus of the M2 EWG (Electronic Standards for the Transfer of Regulatory Information - ESTRI), the E2B(R3) EWG/IWG (Electronic Transmission of Individual Case Safety Reports - ICSR), and the M8 EWG/IWG (Electronic Common Technical Document - eCTD).
Summary
In general, the ICH is essential for promoting the quality, safety, and effectiveness of pharmaceutical products. Its standards provide a framework for standardized and effective development, registration, and post-approval activities, and its focus on harmonization helps to guarantee that patients around the world have access to safe and effective medications.
Additional resources

How to Implement the Continuous Improvement Cycle | Scilife
Even an organization with stellar leadership and a solid core of employees experiences hiccups from time to time. Despite having assembled all the ...

How to assess and enhance your Quality Management Maturity | Scilife
As the life sciences industry becomes increasingly regulated and competitive, quality management has become more vital than ever. Are you confident ...

Best Quality Management Software (QMS) for Life Sciences | Scilife
The right electronic Quality Management System (eQMS) can help strengthen your compliance processes and build a culture of quality within your ...

How to write a good quality plan for medical devices | Scilife
In life sciences, especially if you’re in the medical device industry it becomes harder to manage projects in accordance with your company’s quality ...
Turn quality into your brightest asset with Scilife
