EUDAMED European Database on Medical Devices
Who regulates medical devices? A closer look into EUDAMED
EUDAMED stands for the EU ropean DA tabase on ME dicalDevices. This is a database that monitors the safety and performance of medical devices. EUDAMED’s main goal is to enhance overall transparency by providing better access to information for the public and health care professionals.
To register a medical device in Europe, the manufacturer of the medical device must attach a Global Medical Device Nomenclature (GMDH) code which notifies EUDAMED. The EUDAMED database stores the registration of manufacturers' devices, the device, and the authorized representative (the manufacturer). You can search for the manufacturer certificates on EUDAMED’s public domain.
Why was EUDAMED necessary?
EUDAMED provides centralized management of data that can be readily accessed. EUDAMED ensures the legibility and safety of devices by requiring documentation and certificates. In 2010, an implant company named Poly Implant Prothèse (PIP) illegally manufactured and sold breast implants. The company used cheaper industrial-grade silicone rather than the mandated medical-grade silicone to manufacture their implants. These implants were found to have a 500% higher risk of rupturing and or leaking leading to several deaths and cases of breast cancer. Unfortunately, these implants were sold and distributed for 9 years before a full recall was initiated. At the time, there were no regulated bodies to assess medical devices and share reported incidents efficiently. EUDAMED was formed shortly after with the purpose of strengthening market surveillance and transparency so companies like the Poly Implant Prothèse (PIP) could be held liable.
How does EUDAMED work?
Since the database requires all European medical devices to be registered through EUDAMED, it becomes quite large, as you can imagine. Therefore, it has been split up into 6 different modules: each with its own focus. The first two modules are specifically for manufacturers – registration of economic operators (actor registration) and devices and systems and procedure packs (UDI). The other four modules are notified bodies and certificates, certain aspects of conformity assessment, clinical investigations, vigilance, and market surveillance as well as post-market surveillance.
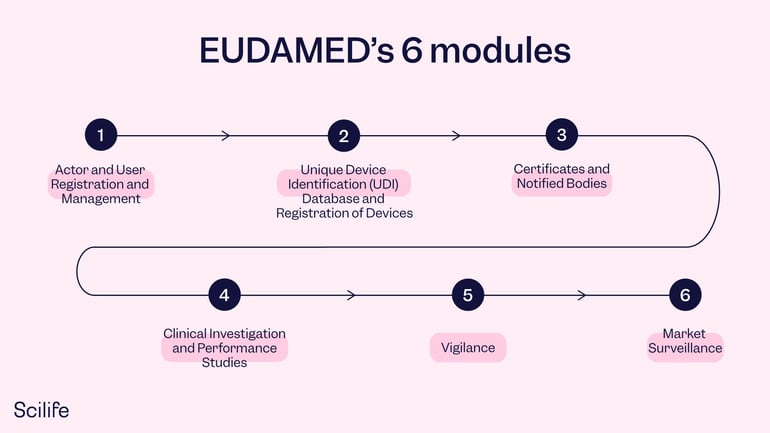
1. Actor and User Registration and Management
Allows manufacturers to register their devices and information.
- First, log in to EUDAMED and request your registration;
- Once you registered, you will receive a single registration number (SRN). Save this number for your record.
- For non-EU medical device manufacturers, its authorized representative authorizes the registration request before sending it to the national competent authority (CA) for evaluation and assessment.
- The national competent authority (CA) allows the SRN to be generated by EUDAMED once they approve the registration request.
- EUDAMED informs the SRN and registration through email to the relevant economic operator
3.Unique Device Identification (UDI) Database and Registration of Devices
Maintains information regarding registered devices 2.
- All devices must have a UDI
- To assign a basic UDI to your medical device, you must fill in the corresponding fields. There are about 20 mandatory fields.
- Now, what if you have 200 medical devices in your portfolio? Do you need to have a UDI for each medical device? Yes! EUDAMED provides an efficient solution for the manufacturer to upload XML files or machine-to-machine communications when there is a large amount of data present.
4.Certificates and Notified Bodies
Stores certificates for each device. This module is publicly available.
5Clinical Investigation and Performance Studies
Maintains information regarding clinical data. Manufacturers must disclose what they would like to achieve before starting the clinical investigation. Most of these studies are visible to the public.
- It is important for the manufacturer to notify EUDAMED 30 days prior to conducting a clinical investigation.
6. Vigilance
Maintains all serious incidents and adverse events. As a healthcare professional, I find this module to be most important for the safety of our patients. EUDAMED mandates manufacturers to report any of the below circumstances
- Medical device problems resulting in an increase in the duration of a surgical procedure
- The manufacturer does not understand the reason of the medical device cause
- Medical device has contributed to death or serious deuteriation in health
- When reporting an incident, manufacturers must report whether they have seen this trend in practice and if this adverse event was included in the device’s product labeling
7.Market Surveillance
Stores post-marketing surveillance of registered devices. It is in the best interest of the manufacturer to register for this module. Market surveillance helps maintain an even playing field for companies that comply with the standards set forth by the EU and identify rogue traders. The authorities help prevent non-compliant products from entering the European market. Additionally, if a medical device is deemed unsafe, the EUDAMED authorities will report it on the safety gate which allows proper dissemination of information to all national authorities. This will help quickly identify the non-compliant products in the market and take measures quickly.
Additional resources

How to Implement the Continuous Improvement Cycle | Scilife
Even an organization with stellar leadership and a solid core of employees experiences hiccups from time to time. Despite having assembled all the ...

How to assess and enhance your Quality Management Maturity | Scilife
As the life sciences industry becomes increasingly regulated and competitive, quality management has become more vital than ever. Are you confident ...

Best Quality Management Software (QMS) for Life Sciences | Scilife
The right electronic Quality Management System (eQMS) can help strengthen your compliance processes and build a culture of quality within your ...

How to write a good quality plan for medical devices | Scilife
In life sciences, especially if you’re in the medical device industry it becomes harder to manage projects in accordance with your company’s quality ...
Turn quality into your brightest asset with Scilife
