When searching for an eQMS (Electronic Quality Management System or Enterprise Quality Management System), it is crucial to prioritize platforms that are purpose-built for meeting the Quality Management Systems (QMS) requirements in the life sciences industry. Basically, a Quality Management System (QMS) is an essential tool for life science companies to ensure consistent quality in their products and services while meeting regulatory requirements. A QMS encompasses a set of documents and processes that help manage quality throughout the organization's operation.
Quality, in this context, refers to meeting applicable requirements, whether they are customer, regulatory, or other related. It involves verifying product attributes, such as appearance and material composition, or adhering to service processes and procedures to meet customer expectations.
In the life sciences industry, the ISO 9001 is a widely used standard for building a robust QMS. It provides a framework for developing a QMS that can be tailored to the specific needs of the organization. ISO 13485, on the other hand, is a spin-off specifically targeted at QMS requirements for medical device manufacturers. Other regulations, such as FDA 21 CFR Part 820 and 21 CFR Part 211, also require life science companies to have a QMS in place.
Implementing a QMS serves the purpose of ensuring consistent quality, especially as the organization grows and needs to verify compliance across its operations. While a paper-based QMS may involve tedious paperwork and documentation, investment in effective eQMS Software can make it less tedious and result in cost savings throughout the business. However, the success of eQMS is also dependent on critical thinking and a vision for quality.
One key aspect of successful eQMS implementation is adopting a risk-based approach to quality. This means integrating risk assessment principles into all core QMS policies and fostering a culture of risk-based thinking. Organizations may seek certification with globally recognized standards like ISO 9001 and ISO 13485, which involves audits and periodic reassessments to ensure compliance and effective implementation of the eQMS.
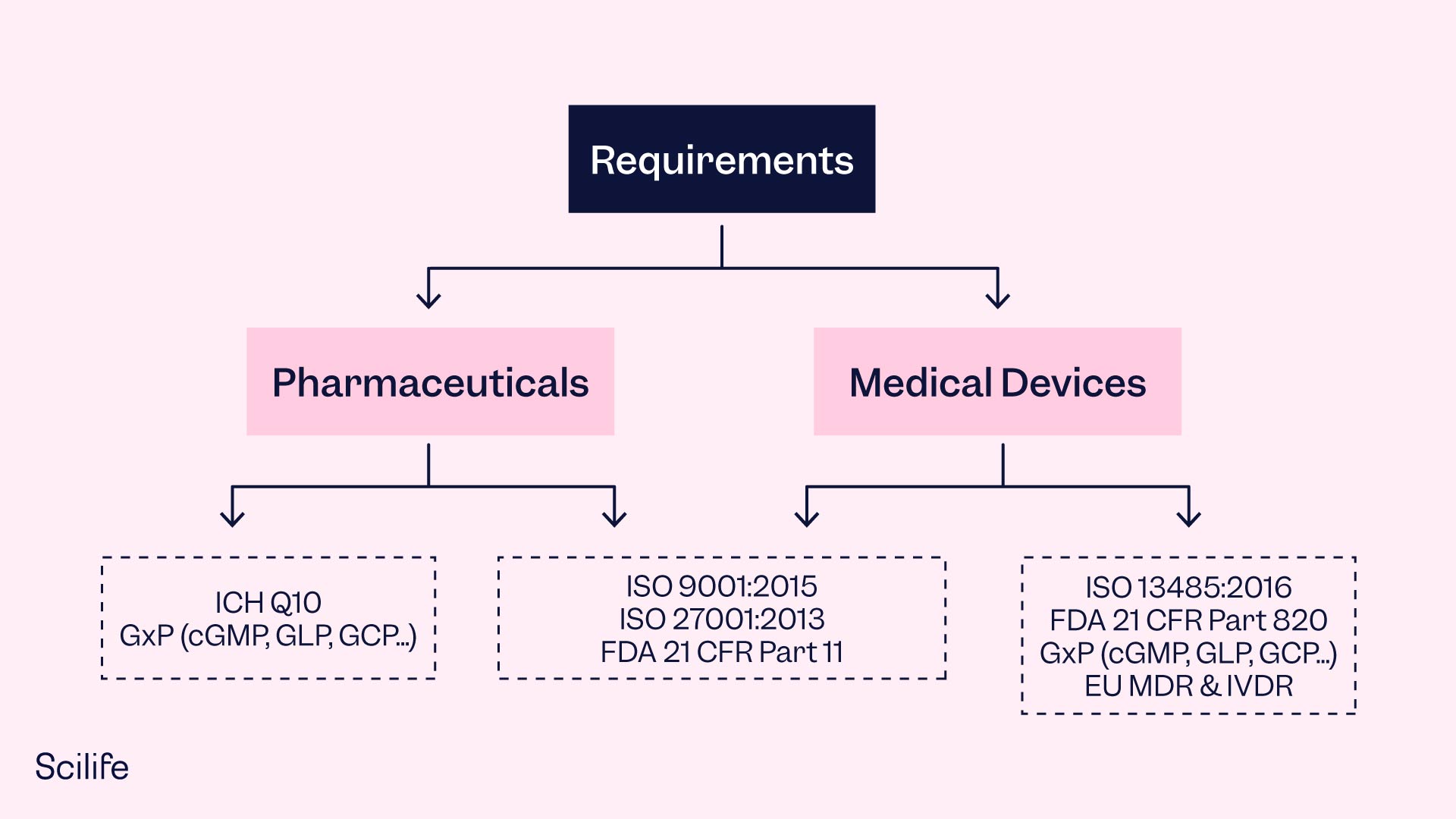
If you are looking to obtain ISO 9001 and ISO 13485 certification you must work on the following aspects to build a robust QMS framework in your organization:
Quality Policy
A guiding principle that defines the company's commitment to quality and sets the tone for the QMS. It should be well-defined, communicated throughout the organization, and publicly posted.
Quality Manual
An overview of the entire QMS that provides a structured understanding of the system, including the scope, requirements, excluded elements, quality procedures, and visual documentation of critical processes.
Quality Objectives
Strategic goals that translate the organization's vision into measurable targets and guide the QMS implementation. Objectives should be realistic, measurable, and periodically revisited.
Organizational Structure and Responsibilities
A clear model of the organization's structure and the responsibilities of individuals within the organization is typically represented through an organizational chart. It should identify the Management Representative responsible for the QMS.
Document and Records Control
Processes to control documents and retain records, including revision control, communication of changes, and retention policies. An electronic QMS can help manage document control effectively.
Processes and Procedures
Standardized, replicable processes throughout the organization, including manufacturing, document control, and purchasing. Processes should be defined, standardized, and continuously improved.
Data Management and Analysis
Collection and analysis of data to make data-driven decisions, identify out-of-control processes, assess quality objectives, and support risk analysis. A quality dashboard can provide a snapshot view of QMS performance.
Continuous Improvement
Utilizing the tools and processes within the QMS for ongoing improvement, innovation, and streamlining of processes. Continuous improvement should be embedded in the culture of the organization.
Building an ISO 9001 and ISO 13485 compliant QMS framework requires careful consideration of the above-mentioned aspects and tailoring them to the specific needs of the organization. It is an ongoing process that involves continuous monitoring, evaluation, and improvement to ensure consistent quality and regulatory compliance.
As a Software as a Service (SaaS) provider that specializes in serving the life sciences industry, we recognize the critical role that an eQMS plays in ensuring compliance, streamlining processes, and maintaining the highest standards of quality. With our extensive experience working with biotech, pharmaceutical, and medical device companies, we have identified the essential elements that every eQMS platform must possess. These elements are non-negotiable and are vital for the success of life sciences organizations.
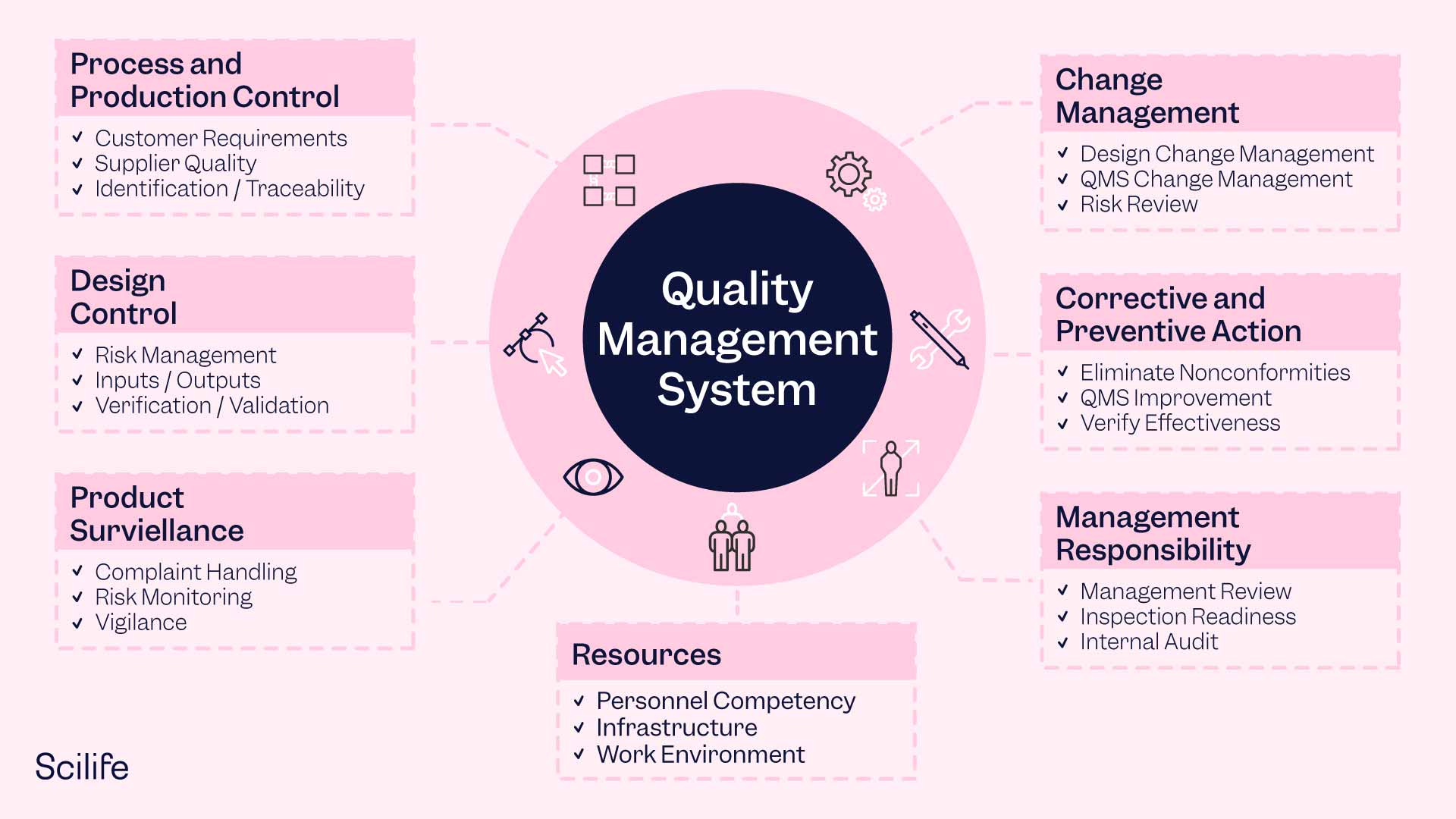
1. Comprehensive Document Control
One of the fundamental requirements of an effective eQMS is comprehensive document control. The life sciences industry operates under strict regulations and standards, necessitating a robust document control system that is flexible enough to handle a wide range of quality, technical, and regulatory documents. This includes features such as strict approval flows, versioning, renditioning, and complex interrelationships, all while maintaining full auditability. It is only with dedicated life science document control solutions that the intricacies of compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GxP) and ISO standards can be fully met.
2. Tailored Training Tools
Life science organizations have unique training requirements that generic training software simply cannot address adequately. An eQMS must provide specialized tools that are tailored to the nuances of the compliance requirements in the life sciences industry. These tools should allow for the creation, deployment, and tracking of training activities specific to different job roles, with a focus on competency validation and accountability. Additionally, the eQMS should incorporate embedded logic to schedule retraining, conduct assessment tests, and provide evidence of completion.
3. Structured CAPA and Nonconformance
Managing nonconformances, deviations, and risk events in the life sciences requires a structured approach. An eQMS must provide compliant and proven frameworks for reporting issues, investigating root causes, determining effective solutions, obtaining necessary approvals, and tracking results over the long term. The embedded logic within the eQMS ensures that all required steps are completed, related to each other, and adequately documented for inspectors. Paper-based QMS often falls short in delivering the necessary related documents for CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Action) and nonconformance management in life science organizations.
4. Advanced Change Control
Change control in the life sciences goes beyond simple approvals and versioning. It encompasses validation, risk assessment, and post-change review. An effective eQMS should offer a step-by-step process for proposing, reviewing, approving, and implementing changes, while also incorporating requirements for justification, validation plans and reports, risk reviews, and effectiveness assessments over time. The complexity and criticality of change control in the life sciences demand an industry-specific design to ensure compliance and maintain the integrity of products and processes.
5. Audit Management
A comprehensive assessment capability is essential for a life science eQMS. It should go beyond simple audit checklists and enable the facilitation and integration of internal audits, external audits, management reviews, risk reviews, and continual improvement initiatives. The eQMS should provide scheduling tools, reporting modules, corrective action handling, and multi-level trending and analysis capabilities over extended periods. A paper-based QMS often requires significant manual effort to manage all the Audit data in GxP environments, making dedicated life science eQMS solutions a necessity.
6. Connected Metrics and Analytics
Quality and compliance metrics alone do not provide sufficient insights for life science leaders. An eQMS should deliver a connected ecosystem of metrics and analytics, providing a single source of truth across various functions such as research and development, quality, manufacturing, and supplier management. It should enable top-down, bottom-up, and cross-functional data aggregation, trending, configuration of key performance indicators (KPIs), and interactive analysis for strategic decision-making. The complex nature of the life sciences industry requires dedicated solutions that can provide actionable insights for informed decision-making.
7. Audits
Audits are a critical aspect of the life sciences industry to ensure compliance with regulations and standards. An eQMS should include robust audit management capabilities that facilitate both internal and external audits. The platform should enable the planning, execution, and tracking of audit activities, as well as the management of audit findings and corrective actions. It should provide tools for generating audit checklists, scheduling audit activities, conducting on-site or remote audits, and generating comprehensive audit reports. The eQMS should also support the integration of audit data with other quality processes, such as CAPA and nonconformance management, to ensure continuous improvement and compliance.
8. Competence Management
Competence management is a vital element of a comprehensive life sciences eQMS platform. Ensuring that employees have the necessary knowledge, skills, and abilities to perform their roles effectively is essential for maintaining quality and compliance in the industry. An eQMS should incorporate competence management tools that enable organizations to assess, develop, and track the competence of their workforce.
The eQMS platform should allow for the creation and management of job-specific competency profiles, outlining the required competencies for different roles within the organization. It should facilitate the assessment of employee competence through various methods, such as training records, performance evaluations, and skills assessments. The platform should also support the identification of competency gaps and provide mechanisms for training and development to address those gaps.
By integrating competence management within the eQMS, organizations can ensure that their employees are adequately trained, competent, and capable of executing their responsibilities in accordance with industry standards and regulations. This helps to mitigate risks, improve operational efficiency, and maintain a culture of quality throughout the organization.
9. Equipment Management
Regular calibration and maintenance of equipment in production units is crucial to ensure its safety and optimal performance. However, the task of managing these activities manually can be overwhelming. Therefore, the implementation of specialized software for equipment calibration and maintenance management is highly recommended. This software enables efficient management of all equipment-related activities, streamlining the process and ensuring compliance with safety standards.
Conclusion
When seeking an eQMS solution for the life sciences industry, it is crucial to consider platforms that offer comprehensive document control, tailored training tools, structured CAPA and nonconformance management, advanced change control, continual assessments, connected metrics and analytics, as well as robust audit management, competence management, and equipment management capabilities. By incorporating all these capabilities, a life sciences eQMS enables organizations to proactively manage their quality processes, identify areas for improvement, and ensure regulatory compliance. These additional elements enhance the overall effectiveness and efficiency of the eQMS, providing organizations with the necessary tools to maintain the highest standards of quality in the ever-evolving life sciences industry.
Purpose-built eQMS platforms designed specifically for the life sciences industry provide the necessary depth, integration, and compliance rigor required to support the complex processes and regulatory requirements of life science organizations. The right eQMS solution can help organizations to maintain the highest level of quality, meet regulatory obligations, and make informed decisions to deliver safe and effective products to patients. Patients deserve nothing less than eQMS excellence, backed by a trusted partner with a commitment to quality. From documents to deviations to data, we understand why every detail matters in the life sciences. Let us work together to get quality done - the right way.






