What is EU GMP Annex 11?
EU GMP rules, also known as the ‘EudraLex rules’ govern the medicinal products in the European Union. The EU GMP rules are split into three different parts plus about 20 annexes. ‘The EU GMP Annex 11’ is one of the supplementary documents of EU GMP rules.
The growing use of computerized systems in life sciences, alongside their intricate structures, has led to the necessity for EU GMP Annex 11 regulations.
EU GMP Annex 11 governs the integrity and security of electronic records and electronic signatures associated with computerized systems. It ensures that replacing a manual operation with a computerized system maintains product quality, process control, and quality assurance. It also ensures that the overall process risk remains at its current level.
Therefore, the purpose of 21 CFR Part 11 and EU Annex 11 is identical, except for the regions in which they are enforced. EU Annex 11 is a regulatory necessity for manufacturers aiming to distribute their products in the European market, while it serves as the equivalent of 21 CFR Part 11, which is mandatory for the US market.
Let’s begin by understanding what kind of computerized systems come under the scope of EU GMP Annex 11. If you'd like to learn more about all the essential pharmaceutical regulations you should know, then go straight to our guide about QMS in pharma.
What is the scope of Annex 11?
Annex 11 applies to all computerized systems that are used as part of GMP-regulated activities. Therefore, all manufacturing and laboratory computerized systems, such as process control systems, digital documentation, data-processing systems, spreadsheets, databases, and statistical analysis software programs come under the purview of EU GMP Annex 11.
Now that we are discussing the scope of EU GMP Annex 11, it would be also worthwhile to know what does not come under the scope of EU GMP Annex 11. Generally speaking, Annex 11 does not apply to medical devices as medical devices are not used in the GMP processes. However, medical device companies can benefit from aligning their activities with guidance to improve future outcomes.
What are the requirements under Annex 11?
The EU Annex 11 is a vast document. It wouldn’t be possible to cover all the requirements under Annex 11 in a blog article. However, we will highlight some key requirements to ensure your electronic records and electronic signatures are EU Annex 11 compliant.
Learn more about the EU GMP Annex 11 by watching our training below:
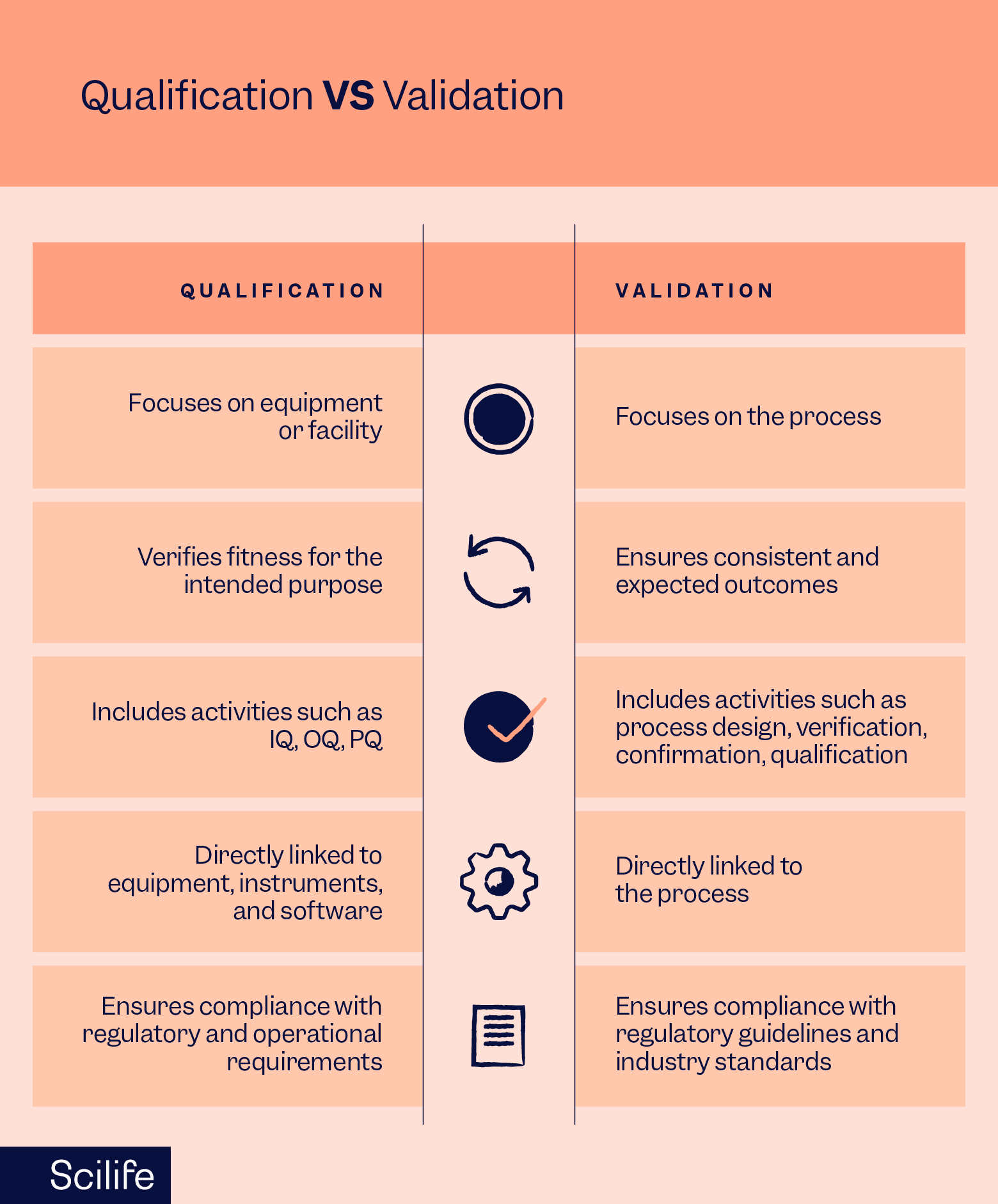
Qualification and Validation
Annex 11 requires all the computerized systems and the IT infrastructure used in GMP-regulated activities to be qualified and validated.
Validation is different from Qualification. Qualification is objective evidence that a piece of equipment or a computerized system has been correctly installed, works as expected, and is fit for the intended use whereas Validation is the assessment and collection of data that establishes objective and scientific evidence that a process, procedure, equipment, material, activity, or system can consistently deliver a quality product.
A lifecycle should be used to validate a system. Annex 11 does not mandate any validation approach; however, the approach selected needs to be justified and documented based on the corresponding risk assessment.
An inventory list of all computerized systems (with a description included for critical systems) should be available during inspections.
For each computerized system validation, there needs to be user requirement specifications that describe the required functions of the system based on risk assessment and GMP impact.
During system validation, test methods and scenarios need to be documented. Testing should include the overall process with consideration to the reporting of quality and performance measures such as data and parameter limits, and with all errors detected and addressed before the system goes live.
Risk management throughout the lifecycle of computerized systems
Annex 11 requires a risk-based approach to be applied throughout the lifecycle of a computerized system to ensure patient safety, data integrity, and product quality. Risk management should be done based on a “justified and documented risk assessment.”
Roles and responsibilities
Managing all electronic records, and electronic signatures about GMP activity cannot be a one-man’s task. Therefore, annex 11 requires close cooperation among key personnel such as users, system administrators, quality assurance team members, and technical staff involved in the development, validation, management, and use of computer systems.
All personnel should have the necessary qualifications, appropriate level of access, and defined responsibilities to carry out their assigned duties. Annex 11 defines the process owner and system owner’s role to enable close cooperation with IT staff and other qualified persons involved in GMP activities. The roles of process owner and system owner are as follows:
- The process owner is the person responsible for the business process. The individual, in this case, is typically a senior manager, as a business process may impact more than one department.
- The system owner is the person responsible for the availability and maintenance of a computerized system and for the security of the data residing on that system (e.g., a senior laboratory manager). The individual, in this case, would go to jail if the system validation is wrong or incomplete.
Suppliers and service providers
Annex 11 requires auditing a service supplier based on a documented and approved risk assessment process. Additionally, in case of non-compliance observations during supplier audits, the organization should monitor the concerned suppliers to ensure corrective and preventive actions have been implemented effectively after the audit.
Apart from this, Annex 11 requires medicinal product manufacturers to enter into a formal agreement outlining the responsibilities of third parties if the latter are hired to supply products or services on a computerized system.
According to Annex 11, even if an organization’s IT department is used to support a validated computerized system, a formal agreement must be in place with the regulated laboratory.
Security Access
For the protection of electronic records and electronic signatures, annex 11 requires security access for authorized employees. The secure access can be provided by the use of a username and password. The security access must be maintained in each validated system.
Further controls are required to protect data from damage. Stored data should be checked for accessibility, readability, and accuracy. This applies to both paper and electronic records.
Electronic signatures
As per Annex 11, electronic signatures must have the same impact as handwritten signatures. They should be permanently linked to the respective record, and include the time and date.
GMP Annex 11 does not share the 21 CFR 11’s formality or stipulation to send letters to the FDA. However, many of the same requirements are implicit, as the European legislation states that all nonrepudiation requirements apply immediately.
Audit trail
Under Annex 11, an audit trail is not mandatory for all computerized systems as the implementation of an audit trail should be based on a documented risk assessment.
We recommend applying audit trails to all electronic data with an impact on product quality, product efficacy, and patient safety. An audit trail needs to include the date and time stamps of record entries, changes, and deletions.
Additionally, the audit trail needs to be available and convertible to an intelligible form. The audit trail should be reviewed regularly to ensure your systems are not merely depositories of unintelligible garbage. You must demonstrate these systems are properly reviewed.
Printouts
The printouts of electronically stored records used to support batch release must show whether any data has been changed since the original entry. This enables a qualified person suitably trained on the job to determine what changes have been made.
Note that only using the audit trail search function to fulfill this requirement is not fully guaranteed. This means you would expect to find the result printed out with an annotation indicating whether the result has been changed.
Archiving process
Section 17 of Annex 11 states that data should be checked for accessibility, readability, and integrity. This means electronic records acquired in one software version can be read in a new version. Therefore, the data should be assessed for “accessibility, readability, and integrity”—especially after changes are made to the backup software or system.
Data storage
Section 7.2 of Annex 11 requires medicinal product manufacturers to regularly backup electronic records about GMP activities. Documented evaluations of the integrity and accuracy of backup data, and the ability to restore data, are also necessary for this purpose.
This last requirement is critical, as it ensures backup media can still be read throughout the record retention period.
Incident management
Under Annex 11 all incidents, system failures, and data errors should be reported and assessed during the system lifecycle. The root cause of a critical incident should be identified and form the basis of corrective and preventive actions.
Incident management implies the need for a process to assess and classify errors. Critical ones require root-cause analysis followed by the formulation of CAPA plans.
Business continuity
EU GMP Annex 11 also has some provisions to ensure business continuity in case of breakdown. In the case of a system breakdown, a backup plan should be available to ensure business continuity and support for critical processes. A backup plan will also help identify the time required to bring alternatives into operation based on risk assessments.
This backup plan should be documented and tested in advance to confirm you have an alternative computer site.
Periodic review
The EU GMP Annex 11 guideline requires the completion of a periodic review to ensure the computerized systems remain in a validated state.
Reviews should cover the last full validation and any changes made in the interim. All deviations and incidents, procedures and training, upgrades, and security need to be documented in a report.
Change and configuration management
According to EU GMP Annex 11 all changes to a computerized system—including system configurations—should only be made in a controlled manner. This ensures the system is maintained in a validation status. A change control procedure must be defined according to risk assessment principles.
Conclusion
In conclusion, achieving compliance with EU GMP Annex 11 for electronic records and electronic signatures is paramount for medicinal product companies operating within the European Union. This regulation serves as a cornerstone for ensuring the integrity, reliability, and security of electronic data in the medicinal product manufacturing process.
By adhering to the guidelines outlined in Annex 11, organizations can enhance data integrity, minimize the risk of errors, and uphold the highest standards of quality and safety in medicinal product manufacturing. Implementing robust systems for electronic recordkeeping and electronic signatures not only helps companies meet regulatory requirements but also fosters efficiency, transparency, and accountability throughout the product lifecycle.
Furthermore, compliance with Annex 11 is not merely a regulatory obligation but also a strategic imperative for medicinal product companies seeking to maintain competitiveness in the global market. Demonstrating a commitment to data integrity and regulatory compliance instills trust among stakeholders, including regulatory authorities, customers, and investors.
The provisions mentioned in the present blog article are not a comprehensive review of the EU GMP Annex 11. Therefore, for a full proof understanding, we also recommend you go through the EU Annex 11 document yourself.
In this dynamic regulatory landscape, staying abreast of updates and advancements in technology is essential for ensuring continued compliance with Annex 11 requirements. By investing in ongoing training, robust IT infrastructure, and proactive risk management strategies, medicinal product companies can navigate the complexities of electronic recordkeeping and electronic signatures while safeguarding product quality and patient safety. Ultimately, compliance with EU GMP Annex 11 is not just a legal requirement but a fundamental element of ensuring public health and maintaining the reputation and integrity of the medicinal product industry.